Abstract
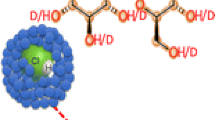
Owing to the development of new ion source technology, users of focused ion beams (FIBs) have access to superior performance when compared with the industry standard Ga+ liquid metal ion source. FIBs equipped with an inductively coupled plasma (ICP) ion source are better able to carry out large volume milling applications by providing up to 2 µA of Xe+ ions focused into a sub-5 µm spot. However, ICP FIBs are presently limited to 25 nm imaging resolution at 1 pA.The gas field ionization source (GFIS) relies upon an ion source that is the size of a single atom and correspondingly gains high brightness through its very small source size. The high brightness allows the GFIS to produce a very small focused probe size (<0.35 nm for helium), but with comparatively small beam currents (less than 2 pA). The Cs+ low temperature ion source, still being developed, has a projected sub-nm focal spot size at 1 pA, a maximum current of several nanoamps, and has the potential to offer integrated secondary ion mass spectrometry capabilities.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Forbes, G.L.R. Mair, in Handbook of Charged Particle Optics, 2nd ed., J. Orloff, Ed. (CRC Press, New York, 2009).
N. Smith, P. Tesch, N. Martin, D. Kinion, Appl. Surf. Sci. 255 (4), 1606 (2008).
N. Smith, P. Tesch, N. Martin, R. Boswell, Micros. Today 17 (5), 18 (2009).
A. Merkulov, P. Peres, J. Choi, F. Horreard, H.-U. Ehrke, N. Loibl, M. Schumacher, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 28, C1 (2010).
P. Hoppe, S. Cohen, A. Meibom, Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 37 (2), 111 (2013).
J. Druce, Kyushu University, personal communication.
F. Altmann, S. Klengel, J. Schischka, M. Petzold, Proc. of 63rd Electronic Components and Technology Conference, ECTC, 1940 (Washington, DC, 2013).
P. Tesch, N. Smith, N. Martin, D. Kinion, Proc. from the 34th International Symposium for Testing and Failure Analysis (ISTFA), 7 (2008).
R. Hill, J. Notte, B. Ward, Phys. Procedia 1, 135 (2008).
B. Knuffman, A.V. Steele, J.J. McClelland, J. Appl. Phys. 114, 044303 (2013).
E.W. Muller, T.T. Tsong, Field Ion Microscopy Principles and Applications (American Elsevier, New York, 1969).
N.P. Economou, J.A. Notte, W.B. Thompson, Scanning 34 (2), 83 (2012).
A.J. Melmed, Appl. Surf. Sci. 94/95, 17 (1996).
R. Hill, J.A. Notte, L. Scipioni, in Advances in Imaging and Electron Physics, P.W. Hawkes, Ed. (Elsevier, New York, 2012), vol. 170, p. 65.
J. Notte, Micros. Today 20 (5), 16 (2012).
H.J. Metcalf, P. van der Straten, Laser Cooling and Trapping (Springer, New York, 1999).
B. Knuffman, A.V. Steele, J. Orloff, J.J. McClelland, New J. Phys. 13, 103035 (2011).
N. Debernardi, M.P. Reijnders, W.J. Engelen, T.T.J. Clevis, P.H.A. Mutsaers, O.J. Luiten, E.J.D. Vredenbregt, J. Appl. Phys. 110, 024501 (2011).
A.V. Steele, B. Knuffman, J.J. McClelland, J. Appl. Phys. 109, 104308 (2011).
P.W. Hawkes, E. Kasper, Principles of Electron Optics, Vol. 2 (Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 1996).
F. Reif, Fundamentals of Statistical and Thermal Physics (Waveland Press, Long Grove, IL, 2009).
S.B. van der Geer, M.P. Reijnders, M.J. deLoos, E.J.D. Vredenbregt, P.H.A. Mutsaers, O.J. Luiten, J. Appl. Phys. 102, 094312 (2007).
A.V. Steele, B. Knuffman, J.J. McClelland, J. Orloff, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 28, C6F1 (2010).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Brenton Knuffman and Jabez McClelland for helpful discussions regarding development of the low-temperature ion source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, N.S., Notte, J.A. & Steele, A.V. Advances in source technology for focused ion beam instruments. MRS Bulletin 39, 329–335 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2014.53
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2014.53