Abstract
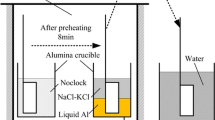
To study the formation mechanism and stability of the phase in the interface of tungsten carbide particles reinforced iron matrix composites, the composites were fabricated by spark plasma sintering (SPS) technique and combined with first-principles calculation. It was found that Fe3W3C compound was stable from the perspective of both thermodynamics and mechanical properties based on our calculations. Interfacial reaction product of tungsten carbide particles reinforced iron matrix composites was M6C. Experimental results indicated that the samples prepared by SPS did not appear interfacial reaction zone, while, interfacial reaction zone appeared for the remelted samples. With the increasing remelting temperature, the width of the interface reaction zone increased because the mutual diffusion occurred at the interface between tungsten carbide particles and matrix. Its formation mechanism was 3Fe + 3/2W2C → Fe3W3C + 1/2C. Our research might provide a theoretical guidance in controlling the interface of tungsten carbide particles reinforced iron matrix composites.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Gassmann: Laser cladding with (WC + W2C)/Co–Cr–C and (WC + W2C)/Ni–B–Si composites for enhanced abrasive wear resistance. Mater. Sci. Technol. 12(8), 691 (1996).
D. Lou, J. Hellman, D. Luhulima, J. Liimatainen, and V. Lindroos: Interactions between tungsten carbide (WC) particulates and metal matrix in WC-reinforced composites. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 340(1), 155 (2003).
T. Fan, Z. Shi, D. Zhang, and R. Wu: The interfacial reaction characteristics in SiC/Al composite above liquidus during remelting. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 257(2), 281 (1998).
O. Liuzhang, L. Chengping, L. Zhuoxuan, and S. Xiandong: Study on interface characteristics of SiCp/ZL109 aluminium alloy composites. Foundry 58(3), 9 (1999).
Z. Liu and X-M. Liu: Effects of interface on wear resistance of fiber reinforced aluminum–silicon alloy composites. Min. Metall. Eng. 23(3), 65 (2003).
Z. Liu and B. Zhou: A study of the interface of short alumina fiber reinforced aluminium alloy composites. Acta Mater. Compositae Sin. 8(4), 1 (1991).
R. Arsenault and N. Shi: Dislocation generation due to differences between the coefficients of thermal expansion. Mater. Sci. Eng. 81, 175 (1986).
R. Arsenault, L. Wang, and C. Feng: Strengthening of composites due to microstructural changes in the matrix. Acta Metall. Mater. 39(1), 47 (1991).
G-S. Zhang, J-D. Xing, and Y-M. Gao: Impact wear resistance of WC/Hadfield steel composite and its interfacial characteristics. Wear 260(7), 728 (2006).
X. You, C. Zhang, N. Liu, M. Huang, and J. Ma: Laser surface melting of electro-metallurgic WC/steel composites. J. Mater. Sci. 43(8), 2929 (2008).
J-P. Gao, Y. Li, S-Z. Wei, W-H. Zhang, and R. Long: Effect of sintering temperature on microstructure and properties of WC steel-bonded cemented carbide/carbon steel composite layer. Mater. Mech. Eng. 1, 005 (2008).
S.Z. Wei, Y. Li, J.P. Gao, Y.P. Ji, and R. Long: Phase structure and microstructure of the interface between WC steel bond hard alloy and carbon steel. In Key Engineering Materials, Vol. 368 (Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland 2008); 1606.
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, and M. Ernzerhof: Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(18), 3865 (1996).
B.G. Pfrommer, M. Côté, S.G. Louie, and M.L. Cohen: Relaxation of crystals with the quasi-Newton method. J. Comput. Phys. 131(1), 233 (1997).
S.F. Matar, R. Weihrich, D. Kurowski, and A. Pfitzner: DFT calculations on the electronic structure of CuTe2 and Cu7Te4. Solid State Sci. 6(1), 15 (2004).
J. Feng, B. Xiao, J. Chen, Y. Du, J. Yu, and R. Zhou: Stability, thermal and mechanical properties of PtxAly compounds. Mater. Des. 32(6), 3231 (2011).
E. Zhao, J. Wang, J. Meng, and Z. Wu: Phase stability and mechanical properties of rhenium borides by first-principles calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 31(9), 1904 (2010).
Y. Li, Y. Gao, B. Xiao, T. Min, Z. Fan, S. Ma, and L. Xu: Theoretical study on the stability, elasticity, hardness and electronic structures of W–C binary compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 502(1), 28 (2010).
S. Patil, S. Khare, B. Tuttle, J. Bording, and S. Kodambaka: Mechanical stability of possible structures of PtN investigated using first-principles calculations. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 73(10), 104118 (2006).
Z-j. Wu, E-j. Zhao, H-p. Xiang, X-f. Hao, X-j. Liu, and J. Meng: Crystal structures and elastic properties of superhard IrN2 and IrN3 from first principles. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 76(5), 054115 (2007).
D. Suetin, I. Shein, and A. Ivanovskii: Structural, electronic and magnetic properties of η carbides (Fe3W3C, Fe6W6C, Co3W3C and Co6W6C) from first principles calculations. Phys. B 404(20), 3544 (2009).
Y. Liu, Y. Jiang, R. Zhou, and J. Feng: Mechanical properties and chemical bonding characteristics of WC and W2C compounds. Ceram. Int. 40(2), 2891 (2014).
Y. Liang and Y. Che: Handbook of Thermodynamic Data for Inorganic Material (Northeast University Press, China, 1993).
Q-B. Yang and S. Andersson: Application of coincidence site lattices for crystal structure description. Part I: Σ = 3. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Sci. 43(1), 1 (1987).
Y. Liu, Y. Jiang, R. Zhou, and J. Feng: First-principles calculations of the mechanical and electronic properties of Fe–W–C ternary compounds. Comput. Mater. Sci. 82, 26 (2014).
Y. Li, Y. Gao, Z. Fan, B. Xiao, Q. Yue, T. Min, and S. Ma: First-principles study on the stability and mechanical property of eta M3W3C (M = Fe, Co, Ni) compounds. Phys. B 405(3), 1011 (2010).
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos: 51361019 and 51561018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Wei, H., Shan, Q. et al. Formation mechanism and stability of the phase in the interface of tungsten carbide particles reinforced iron matrix composites: First principles calculations and experiments. Journal of Materials Research 31, 2376–2383 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.268
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.268