Abstract
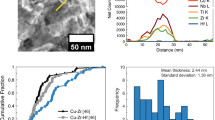
Grain boundary (GB) segregation can markedly improve the stability of nanostructured alloys, where the fraction of GB sites is inherently large. Here, we explore the concept of entropically supported GB segregation in alloys with a tendency to phase-separate and its role in stabilizing nanostructures therein. These duplex nanocrystalline alloys are notably different, both in a structural and thermodynamic sense, from the previously studied “classical” nanocrystalline alloys, which are solid solutions with GB segregation of solute. Experiments are conducted on the W–Cr system, in which nanoduplex structures are expected. Upon heating ball-milled W–15 at.% Cr up to 950 °C, a nanoscale Cr-rich phase was found along the GBs. These precipitates mostly dissolved into the W-rich grains leaving behind Cr-enriched GBs upon further heating to 1400 °C. The presence of Cr-rich nanoprecipitates and GB segregation of Cr is in line with prediction from our Monte Carlo simulation when GB states are incorporated into the alloy thermodynamics.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Zhao, D.W. He, L.L. Daemen, T.D. Shen, R.B. Schwarz, Y. Zhu, D.L. Bish, J. Huang, J. Zhang, G. Shen, J. Qian, and T.W. Zerda: Superhard B–C–N materials synthesized in nanostructured bulks. J. Mater. Res. 17(12), 3139 (2002).
Y. Lei, Y. Ito, N.D. Browning, and T.J. Mazanec: Segregation effects at grain boundaries in fluorite-structured ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85(9), 2359 (2002).
U. Anselmi-Tamburini, J.E. Garay, Z.A. Munir, A. Tacca, F. Maglia, G. Chiodelli, and G. Spinolo: Spark plasma sintering and characterization of bulk nanostructured fully stabilized zirconia: Part II. Characterization studies. J. Mater. Res. 19(11), 3263 (2004).
K. Matsui, N. Ohmichi, M. Ohgai, H. Yoshida, and Y. Ikuhara: Effect of alumina-doping on grain boundary segregation-induced phase transformation in yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal. J. Mater. Res. 21(09), 2278 (2006).
T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, M.D. Pickett, M. Heuer, J.P. Kalejs, G. Hahn, M.A. Marcus, B. Lai, Z. Cai, S.M. Heald, T.F. Ciszek, R.F. Clark, D.W. Cunningham, A.M. Gabor, R. Jonczyk, S. Narayanan, E. Sauar, and E.R. Weber: Chemical natures and distributions of metal impurities in multicrystalline silicon materials. Prog. Photovoltaics 14(6), 513 (2006).
K. Biswas, J. He, I.D. Blum, C-I. Wu, T.P. Hogan, D.N. Seidman, V.P. Dravid, and M.G. Kanatzidis: High-performance bulk thermoelectrics with all-scale hierarchical architectures. Nature 489(7416), 414 (2012).
S. Bechtle, M. Kumar, B.P. Somerday, M.E. Launey, and R.O. Ritchie: Grain-boundary engineering markedly reduces susceptibility to intergranular hydrogen embrittlement in metallic materials. Acta Mater. 57(14), 4148 (2009).
T. Watanabe and S. Tsurekawa: The control of brittleness and development of desirable mechanical properties in polycrystalline systems by grain boundary engineering. Acta Mater. 47(15–16), 4171 (1999).
T.D. Shen, R.B. Schwarz, S. Feng, J.G. Swadener, J.Y. Huang, M. Tang, J. Zhang, S.C. Vogel, and Y. Zhao: Effect of solute segregation on the strength of nanocrystalline alloys: Inverse Hall–Petch relation. Acta Mater. 55(15), 5007 (2007).
H-P. Chen, R.K. Kalia, E. Kaxiras, G. Lu, A. Nakano, K-i. Nomura, A.C. van Duin, P. Vashishta, and Z. Yuan: Embrittlement of metal by solute segregation-induced amorphization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104(15), 155502 (2010).
J. Luo, H. Cheng, K.M. Asl, C.J. Kiely, and M.P. Harmer: The role of a bilayer interfacial phase on liquid metal embrittlement. Science 333(6050), 1730 (2011).
Y.J. Li, P. Choi, S. Goto, C. Borchers, D. Raabe, and R. Kirchheim: Evolution of strength and microstructure during annealing of heavily cold-drawn 6.3 GPa hypereutectoid pearlitic steel wire. Acta Mater. 60(9), 4005 (2012).
M. Herbig, D. Raabe, Y. Li, P. Choi, S. Zaefferer, and S. Goto: Atomic-scale quantification of grain boundary segregation in nanocrystalline material. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112(12), 126103 (2014).
I. Povstugar, P-P. Choi, S. Neumeier, A. Bauer, C.H. Zenk, M. Göken, and D. Raabe: Elemental partitioning and mechanical properties of Ti- and Ta-containing Co–Al–W-base superalloys studied by atom probe tomography and nanoindentation. Acta Mater. 78, 78 (2014).
T. Chookajorn and C.A. Schuh: Nanoscale segregation behavior and high-temperature stability of nanocrystalline W–20 at.% Ti. Acta Mater. 73, 128 (2014).
A.J. Detor and C.A. Schuh: Microstructural evolution during the heat treatment of nanocrystalline alloys. J. Mater. Res. 22(11), 3233 (2007).
S-Y. Choi, D-Y. Yoon, and S-J.L. Kang: Kinetic formation and thickening of intergranular amorphous films at grain boundaries in barium titanate. Acta Mater. 52(12), 3721 (2004).
S. Ruan, K.L. Torres, G.B. Thompson, and C.A. Schuh: Gallium-enhanced phase contrast in atom probe tomography of nanocrystalline and amorphous Al–Mn alloys. Ultramicroscopy 111(8), 1062 (2011).
C.A. Schuh, M. Kumar, and W.E. King: Analysis of grain boundary networks and their evolution during grain boundary engineering. Acta Mater. 51(3), 687 (2003).
S. Zheng, I.J. Beyerlein, J.S. Carpenter, K. Kang, J. Wang, W. Han, and N.A. Mara: High-strength and thermally stable bulk nanolayered composites due to twin-induced interfaces. Nat. Commun. 4, 1696 (2013).
S. Zheng, J.S. Carpenter, R.J. McCabe, I.J. Beyerlein, and N.A. Mara: Engineering interface structures and thermal stabilities via SPD processing in bulk nanostructured metals. Sci. Rep. 4, 1–6 (2014).
O.K. Johnson and C.A. Schuh: The triple junction hull: Tools for grain boundary network design. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 69, 2 (2014).
I.J. Beyerlein, X. Zhang, and A. Misra: Growth twins and deformation twins in metals. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 44(1), 329 (2014).
J. Weissmüller: Alloy effects in nanostructures. Nanostruct. Mater. 3(1–6), 261 (1993).
J. Weissmüller: Alloy thermodynamics in nanostructures. J. Mater. Res. 9(01), 4 (1994).
J. Weissmüller: Some basic notions on nanostructured solids. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 179, 102 (1994).
R. Kirchheim: Grain coarsening inhibited by solute segregation. Acta Mater. 50(2), 413 (2002).
R. Kirchheim: Reducing grain boundary, dislocation line and vacancy formation energies by solute segregation. I. Theoretical background. Acta Mater. 55(15), 5129 (2007).
R. Kirchheim: Reducing grain boundary, dislocation line and vacancy formation energies by solute segregation: II. Experimental evidence and consequences. Acta Mater. 55(15), 5139 (2007).
P.C. Millett, R.P. Selvam, S. Bansal, and A. Saxena: Atomistic simulation of grain boundary energetics–Effects of dopants. Acta Mater. 53(13), 3671 (2005).
P.C. Millett, R.P. Selvam, and A. Saxena: Molecular dynamics simulations of grain size stabilization in nanocrystalline materials by addition of dopants. Acta Mater. 54(2), 297 (2006).
P.C. Millett, R.P. Selvam, and A. Saxena: Stabilizing nanocrystalline materials with dopants. Acta Mater. 55(7), 2329 (2007).
D. Raabe, M. Herbig, S. Sandlöbes, Y. Li, D. Tytko, M. Kuzmina, D. Ponge, and P.P. Choi: Grain boundary segregation engineering in metallic alloys: A pathway to the design of interfaces. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 18(4), 253 (2014).
M. Tang, W.C. Carter, and R.M. Cannon: Grain boundary transitions in binary alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97(7), 075502 (2006).
S.J. Dillon, M. Tang, W.C. Carter, and M.P. Harmer: Complexion: A new concept for kinetic engineering in materials science. Acta Mater. 55(18), 6208 (2007).
M. Baram, D. Chatain, and W.D. Kaplan: Nanometer-thick equilibrium films: The interface between thermodynamics and atomistics. Science 332(6026), 206 (2011).
D. Raabe, S. Sandlöbes, J. Millán, D. Ponge, H. Assadi, M. Herbig, and P.P. Choi: Segregation engineering enables nanoscale martensite to austenite phase transformation at grain boundaries: A pathway to ductile martensite. Acta Mater. 61(16), 6132 (2013).
W. Han, M.J. Demkowicz, N.A. Mara, E. Fu, S. Sinha, A.D. Rollett, Y. Wang, J.S. Carpenter, I.J. Beyerlein, and A. Misra: Design of radiation tolerant materials via interface engineering. Adv. Mater. 25(48), 6975 (2013).
P.R. Cantwell, M. Tang, S.J. Dillon, J. Luo, G.S. Rohrer, and M.P. Harmer: Grain boundary complexions. Acta Mater. 62, 1 (2014).
F. Baletto and R. Ferrando: Structural properties of nanoclusters: Energetic, thermodynamic, and kinetic effects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77(1), 371 (2005).
X. Dou, G. Li, and H. Lei: Kinetic versus thermodynamic control over growth process of electrodeposited Bi/BiSb superlattice nanowires. Nano Lett. 8(5), 1286 (2008).
J.J. Vajo: Influence of nano-confinement on the thermodynamics and dehydrogenation kinetics of metal hydrides. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 15(2), 52 (2011).
T. Chookajorn, H.A. Murdoch, and C.A. Schuh: Design of stable nanocrystalline alloys. Science 337(6097), 951 (2012).
H.A. Murdoch and C.A. Schuh: Stability of binary nanocrystalline alloys against grain growth and phase separation. Acta Mater. 61(6), 2121 (2013).
T. Chookajorn and C.A. Schuh: Thermodynamics of stable nanocrystalline alloys: A Monte Carlo analysis. Phys. Rev. B 89(6), 064102 (2014).
T. Chookajorn: Enhancing stability of powder-route nanocrystalline tungsten-titanium via alloy thermodynamics. In Department of Materials Science and Engineering (Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, 2013).
R. Kirchheim: Comment on “Unexplored topics and potentials of grain boundary engineering” by L.S. Shvindlerman and G. Gottstein. Scr. Mater. 55(10), 963 (2006).
G. Gottstein and L.S. Shvindlerman: Reply to comments on “Unexplored topics and potentials of grain boundary engineering”. Scr. Mater. 55(10), 965 (2006).
P.E.A. Turchi, L. Kaufman, and Z.K. Liu: Modeling of Ni-Cr-Mo based alloys: Part I—phase stability. CALPHAD: Comput. Coupling Phase Diagrams Thermochem. 30(1), 70 (2006).
Z.C. Cordero and C.A. Schuh: Phase strength effects on chemical mixing in extensively deformed alloys. Acta Mater. 82, 123 (2015).
M. Park and C.A. Schuh: Mechanism to accelerate sintering in phase-separating nanostructured alloys. Manuscript presently under review.
D.C. Joy, A.D. Romig, and J. Goldstein: Principles of Analytical Electron Microscopy (Springer, New York, 1986).
G. Lorimer: Quantitative X-ray microanalysis of thin specimens in the transmission electron microscope; a review. Mineral. Mag. 51(359), 49 (1987).
S-J. Shih, S. Lozano-Perez, and D.J.H. Cockayne: Investigation of grain boundaries for abnormal grain growth in polycrystalline SrTiO3. J. Mater. Res. 25(02), 260 (2010).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the US Army Research Office under Grants No. W911NF-09-1-0422 and W911NF-14-1-0539, and by the US Defense Threat Reduction Agency under Grant No. HDTRA1-11-1-0062. M.P. acknowledges support through a Kwan-Jung scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contributing Editor: Suk-Joong L. Kang
This paper has been selected as an Invited Feature Paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chookajorn, T., Park, M. & Schuh, C.A. Duplex nanocrystalline alloys: Entropic nanostructure stabilization and a case study on W–Cr. Journal of Materials Research 30, 151–163 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.385
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.385