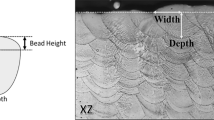
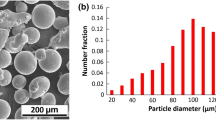
Abstract
Cube-shaped IN718 samples were produced by selective electron beam melting (SEBM) with varying beam power, deflection speed, and beam spot size. Process parameter windows were identified where fully dense samples are obtained with no surface unevenness. High deflection speeds were demonstrated to result in smaller demand of area energy. This result is explained by the reduced time for heat dissipation into the substrate during hatching. The grain structure was strongly affected by SEBM process parameters. Under certain conditions, epitaxial growth over many layers and well-developed columnar grain structures were obtained with a polycrystalline substrate plate. A more defocused beam led to a lower melt pool temperature and shallower melt pool geometry where maximum temperature gradients and solidification rates were more or less in parallel with the building direction and primary dendrite arm orientation. These conditions help to suppress grain nucleation ahead of the nucleation front as vigorous melt movement, fragmentation of dendrites, and tertiary arm growth are suppressed.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Hopkinson, R. Hague, and P. Dickens: Rapid Manufacturing: An Industrial Revolution for the Digital Age, 1st ed. (Wiley, Camberley, England, 2006).
P. Blackwell: The mechanical and microstructural characteristics of laser-deposited IN718. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 170(1–2), 240 (2005).
A. Strondl, R. Fischer, G. Frommeyer, and A. Schneider: Investigations of MX and γ′/γ″ precipitates in the nickel-based superalloy 718 produced by electron beam melting. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 480(1–2), 138 (2008).
A. Strondl, M. Palm, J. Gnauk, and G. Frommeyer: Microstructure and mechanical properties of nickel based superalloy IN718 produced by rapid prototyping with electron beam melting (EBM). Mater. Sci. Technol. 27(5), 876 (2009).
A. Strondl, S. Milenkovic, A. Schneider, U. Klement, and G. Frommeyer: Effect of processing on microstructure and physical properties of three nickel-based superalloys with different hardening mechanisms. Adv. Eng. Mater. 14(7), 427 (2012).
K.N. Amato, S.M. Gaytan, L.E. Murr, E. Martinez, P.W. Shindo, J. Hernandez, S. Collins, and F.R. Medina: Microstructures and mechanical behavior of Inconel 718 fabricated by selective laser melting. Acta Mater. 60(5), 2229 (2012).
Z. Wang, K. Guan, M. Gao, X. Li, X. Chen, and X. Zeng: The microstructure and mechanical properties of deposited-IN718 by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 513(0), 518 (2012).
P. Heinl, L. Müller, C. Körner, R.F. Singer, and F.A. Müller: Cellular Ti–6Al–4V structures with interconnected macro porosity for bone implants fabricated by selective electron beam melting. Acta Biomater. 4(5), 1536 (2008).
X. Zhao, J. Chen, X. Lin, and W. Huang: Study on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser rapid forming Inconel 718. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 478(1–2), 119 (2008).
H. Qi, M. Azer, and A. Ritter: Studies of standard heat treatment effects on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser net shape manufactured INCONEL 718. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 40(10), 2410–2422 (2009).
A. Klassen, T. Scharowsky, and C. Körner: Evaporation model for beam based additive manufacturing using free surface lattice Boltzmann methods. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 47(27), 275 (2014).
H.S. Carslaw and J.C. Jaeger: Conduction of Heat in Solids, 2nd ed. (Oxford University Press, New York, 1959), pp. 58–62.
G. Pottlacher, H. Hosaeus, E. Kaschnitz, and A. Seifter: Thermophysical properties of solid and liquid Inconel 718 alloy. Scand. J. Metall. 31(3), 161 (2002).
R. Ito, P. Andreo, and T. Tabata: Reflection ratios of electrons and photons from solids. Bull. Univ. Osaka Prefect., Ser. A 41(2), 69 (1992).
T. Tabata, P. Andreo, and K. Shinoda: Fractional energies of backscattered electrons and photon yields by electrons. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 54(1), 11 (1999).
D. Walton and B. Chalmers: The origin of the preferred orientation in the columnar zone of ingots. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 215(6), 1 (1959).
M. Gäumann, C. Bezençon, P. Canalis, and W. Kurz: Single-crystal laser deposition of superalloys: Processing–microstructure maps. Acta Mater. 49(6), 1051 (2001).
L. Thijs, F. Verhaeghe, T. Craeghs, J.V. Humbeeck, and J.P. Kruth: A study of the microstructural evolution during selective laser melting of Ti-6Al-4V. Acta Mater. 58(9), 3303 (2010).
M. Gäumann, S. Henry, F. Cléton, J-D. Wagnière, and W. Kurz: Epitaxial laser metal forming: Analysis of microstructure formation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 271(1–2), 232 (1999).
R. Trivedi and W. Kurz: Dendritic growth. Int. Mater. Rev. 39(2), 49 (1994).
M. Rappaz, S.A. David, J.M. Vitek, and L.A. Boatner: Development of microstructures in Fe−15Ni−15Cr single crystal electron beam welds. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 20(6), 1125 (1989).
M. Rappaz, S.A. David, J.M. Vitek, and L.A. Boatner: Analysis of solidification microstructures in Fe-Ni-Cr single-crystal welds. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 21(6), 1767 (1990).
S. Mokadem, C. Bezençon, A. Hauert, A. Jacot, and W. Kurz: Laser repair of superalloy single crystals with varying substrate orientations. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 38(7), 1500 (2007).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge funding by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) through the Collaborative Research Center SFB/Transregio 103, Project B2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helmer, H.E., Körner, C. & Singer, R.F. Additive manufacturing of nickel-based superalloy Inconel 718 by selective electron beam melting: Processing window and microstructure. Journal of Materials Research 29, 1987–1996 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.192
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.192