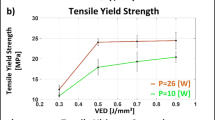
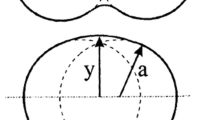
Abstract
High Speed Sintering (HSS) is a novel additive manufacturing technology which currently uses Nylon 12 as the standard feedstock material. To expand the number of processable materials, the preferred characteristics of polymeric powder as a feedstock powder are presented, appropriate materials identified, parts made, and mechanical properties measured. Two commercially available laser sintering (LS) grade powders previously untested for HSS were selected, DuraForm® HST10 and ALM TPE 210-S. Tensile test specimens were manufactured using each material and mechanical properties analyzed and compared to the manufacturers’ specification for LS. Tensile test specimens built using DuraForm® PA show higher tensile strength and elongation at break than LS whereas DuraForm® HST10 shows somewhat reduced tensile strength but slightly increased elongation at break. ALM TPE 210-S shows elongation at break of more than double that of LS demonstrating the capability of HSS to process viscous materials. The results indicate that HSS is capable of processing LS grade polymeric powders and may extend beyond.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Hopkinson and P. Erasenthiran: High speed sintering–Early research into a new rapid manufacturing process. In Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium (University of Texas, Austin, 2004); pp. 312–320.
H.R. Thomas, N. Hopkinson, and P. Erasenthiran: High speed sintering–Continuing research into a new rapid manufacturing process. In Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium (University of Texas, Austin, 2006); pp. 682–691.
N. Hopkinson, R. Hague, and P. Dickens: Rapid Manufacturing: An Industrial Revolution for the Digital Age (John Wiley & Sons, West Sussex, UK, 2006).
S. Gogolewski, K. Czerntawska, and M. Gastorek: Effect of annealing on thermal properties and crystalline structure of polyamides. Nylon 12 (polylaurolactam). Colloid Polym. Sci. 258(10), 1130–1136 (1980).
Y. Kong and J.N. Hay: The enthalpy of fusion and degree of crystallinity of polymers as measured by DSC. Eur. Polym. J. 39(8), 1721–1727 (2003).
M. Vasquez, B. Haworth, and N. Hopkinson: Optimum sintering region for laser sintered nylon-12. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part B 225(12), 2240–2248 (2011).
C.E. Majewski, D. Oduye, H.R. Thomas, and N. Hopkinson: Effect of infra-red power level on the sintering behaviour in the high speed sintering process. Rapid Prototyping J. 14(3), 155–160 (2008).
S.K. Tiwari and S. Pande: Material properties and selection for selective laser sintering process. Int. J. Manuf. Tech. Manag. 27(4), 198–217 (2013).
Y. Shi, Z. Li, H. Sun, S. Huang, and F. Zeng: Effect of the properties of the polymer materials on the quality of selective laser sintering parts. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part L 218(3), 247–252 (2004).
C.A. Harper: Handbook of Plastics, Elastomers, and Composites (McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 2002).
T. Wohlers: Wohlers Report 2007: State of the Industry: Annual Worldwide Progress Report (Wohlers Associates, Inc., Fort Collins, CO, 2007).
C.E. Majewski, B.S. Hobbs, and N. Hopkinson: Effect of bed temperature and infra-red lamp power on the mechanical properties of parts produced using high-speed sintering. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2(2), 103–110 (2007).
I. Gibson and D. Shi: Material properties and fabrication parameters in selective laser sintering process. Rapid Prototyping J. 3(4), 129–136 (1997).
B. Caulfield, P. McHugh, and S. Lohfeld: Dependence of mechanical properties of polyamide components on build parameters in the SLS process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 182(1), 477–488 (2007).
H. Zarringhalam, N. Hopkinson, N.F. Kamperman, and J.J. De Vlieger: Effects of processing on microstructure and properties of SLS Nylon 12. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 435, 172–180 (2006).
ASTM D638: Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics.
C. Majewski, H. Zarringhalam, and N. Hopkinson: Effect of the degree of particle melt on mechanical properties in selective laser-sintered Nylon-12 parts. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part B 222(9), 1055–1064 (2008).
C. Majewski, H. Zarringhalam, and N. Hopkinson: Effects of degree of particle melt and crystallinity in SLS Nylon-12 parts. In 19th Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium (University of Texas, Austin, 2008).
E. Moeskops, N. Kamperman, and B. van de Vorst: Creep behaviour of polyamide in selective laser sintering. In Proceedings of the 15th Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, ASTM D638-10, Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA (University of Texas, Austin, 2004).
B. Haworth, N. Hopkinson, D. Hitt, and X. Zhong: Shear viscosity measurements on Polyamide-12 polymers for laser sintering. Rapid Prototyping J. 19(1), 28–36 (2013).
J. Frenkel: Viscous flow of crystalline bodies under the action of surface tension. J. Phys. 9, 385 (1945).
G.M. Vasquez: Analysis and Development of New Materials for Polymer Laser Sintering (Loughborough University, UK, 2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellis, A., Noble, C.J., Hartley, L. et al. Materials for high speed sintering. Journal of Materials Research 29, 2080–2085 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.156
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.156