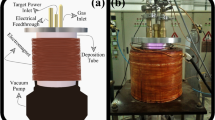
Abstract
High-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) is a promising sputtering-based ionized physical vapor deposition technique and is already making its way to industrial applications. The major difference between HiPIMS and conventional magnetron sputtering processes is the mode of operation. In HiPIMS the power is applied to the magnetron (target) in unipolar pulses at a low duty factor (<10%) and low frequency (<10 kHz) leading to peak target power densities of the order of several kilowatts per square centimeter while keeping the average target power density low enough to avoid magnetron overheating and target melting. These conditions result in the generation of a highly dense plasma discharge, where a large fraction of the sputtered material is ionized and thereby providing new and added means for the synthesis of tailor-made thin films. In this review, the features distinguishing HiPIMS from other deposition methods will be addressed in detail along with how they influence the deposition conditions, such as the plasma parameters and the sputtered material, as well as the resulting thin film properties, such as microstructure, phase formation, and chemical composition. General trends will be established in conjunction to industrially relevant material systems to present this emerging technology to the interested reader.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ohring: Materials Science of Thin Films (Academic Press, San Diego, 2002).
F.M. Penning, U.S. Patent No: 2,146,025 (1939) (German Patent filed 1935).
J.A. Thornton and A.S. Penfold: Cylindrical magnetron sputtering in thin film processes. Thin Film Processes, edited by J.L. Vossen and W. Kern (Academic Press, New York, 1978).
V. Kouznetsov, K. Macák, J.M. Schneider, U. Helmersson, and I. Petrov: A novel pulsed magnetron sputter technique utilizing very high target power densities. Surf. Coat. Tech. 122, 290 (1999).
U. Helmersson, M. Lattemann, J. Bohlmark, A.P. Ehiasarian, and J.T. Gudmundsson: Ionized physical vapor deposition (IPVD): A review of technology and applications. Thin Solid Films 513, 1 (2006).
A. Anders: Discharge physics of high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Tech. 205, S1 (2011).
J. Bohlmark, M. Lattemann, J.T. Gudmundsson, A.P. Ehiasarian, Y. Aranda Gonzalvo, N. Brenning, and U. Helmersson: The ion-energy distributions and plasma composition of a high power impulse magnetron sputtering discharge. Thin Solid Films 515, 1522 (2006).
M. Samuelsson, D. Lundin, J. Jensen, M.A. Raadu, J.T. Gudmundsson, and U. Helmersson: On the film density using high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Tech. 15, 591 (2010).
V. Sittinger, F. Ruske, W. Werner, C. Jacobs, B. Szyszka, and D. Christie: High power pulsed magnetron sputtering of transparent conducting oxides. Thin Solid Films 516, 5847 (2008).
M. Lattemann, U. Helmersson, and J.E. Greene: Fully dense, non-faceted 111-textured high power impulse magnetron sputtering TiN films grown in the absence of substrate heating and bias. Thin Solid Films 518, 5978 (2010).
S. Konstantinidis, J.P. Dauchot, and M. Hecq: Titanium oxide thin films deposited by high-power impulse magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 515, 1182 (2006).
J. Alami, P. Eklund, J.M. Andersson, M. Lattemann, E. Wallin, J. Bohlmark, P. Persson, and U. Helmersson: Phase tailoring of Ta thin films by highly ionized pulsed magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 515, 3434 (2007).
J. Paulitsch, P.H. Mayrhofer, C. Mitterer, W-D. Münz, and M. Schenkel: Mechanical and tribological properties of CrN coatings deposited by a simultaneous HIPIMS/UBM sputtering process, in Society of Vacuum Coaters 50th Annual Technical Conference Proceedings, April 28–May 3 (Louisville, KY, 2007), p. 150.
A.P. Ehiasarian, J.G. Wen, and I. Petrov: Interface microstructure engineering by high power impulse magnetron sputtering for the enhancement of adhesion. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 054301 (2007).
J. Alami, P.O.Å. Persson, D. Music, J.T. Gudmundsson, J. Bohlmark, and U. Helmersson: Ion-assisted physical vapor deposition for enhanced film properties on nonflat surfaces. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 23, 278 (2005).
A. Aijaz, D. Lundin, P. Larsson, and U. Helmersson: Dual-magnetron open field sputtering system for sideways deposition of thin films. Surf. Coat. Tech. 204, 2165 (2010).
E. Wallin, T.I. Selinder, M. Elfwing, and U. Helmersson: Synthesis of α-Al2O3 thin films using reactive high-power impulse magnetron sputtering. Europhys. Lett. 82, 36002 (2008).
K. Sarakinos, J. Alami, and S. Konstantinidis: High power pulsed magnetron sputtering: A review on scientific and engineering state of the art. Surf. Coat. Tech. 204, 1661 (2010).
C. Christou and Z.H. Barber: Ionization of sputtered material in a planar magnetron discharge. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 18, 2897 (2000).
S.M. Rossnagel and J. Hopwood: Metal ion deposition from ionized magnetron sputtering discharge. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 12, 449 (1994).
S. Konstantinidis, A. Ricard, M. Ganciu, J.P. Dauchot, C. Ranea, and M. Hecq: Measurement of ionic and neutral densities in amplified magnetron discharges by pulsed absorption spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 2900 (2004).
C. Nouvellon, S. Konstantinidis, J.P. Dauchot, M. Wautelet, P.Y. Jouan, A. Ricard, and M. Hecq: Emission spectrometry diagnostic of sputtered titanium in magnetron amplified discharges. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 32 (2002).
C.P. Johnson: The cathodic arc plasma deposition of thin films, in J.L. Vossen and W. Kern (eds.): Thin Film Processes II (Academic Press, New York, 1991).
W.D. Davis and H.C. Miller: Analysis of the electrode products emitted by dc arcs in a vacuum ambient. J. Appl. Phys. 40, 2212 (1969).
Z. Wang and S.A. Cohen: Hollow cathode magnetron. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 17, 77 (1999).
E. Klawuhn, G.C. D’Couto, K.A. Ashtiani, P. Rymer, M.A. Biberger, and K.B. Levy: Ionized physical-vapor deposition using a hollow-cathode magnetron source for advanced metallization. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 18, 1546 (2000).
D. Söderström: Modelling and Applications of the Hollow Cathode Plasma. Doctoral Thesis, Uppsala University, Uppsala, (2008).
S. Konstantinidis, J.P. Dauchot, M. Ganciu, A. Ricard, and M. Hecq: Influence of pulse duration on the plasma characteristics in high-power pulsed magnetron discharges. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 013307 (2006).
D. Lundin, N. Brenning, D. Jädernäs, P. Larsson, E. Wallin, M. Lattemann, M.A. Raadu, and U. Helmersson: Transition between the discharge regimes of high power impulse magnetron sputtering and conventional direct current magnetron sputtering. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 18, 045008 (2009).
E. Wallin and U. Helmersson: Hysteresis-free reactive high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 516, 6398 (2008).
J. Alami, K. Sarakinos, F. Uslu, and M. Wuttig: On the relationship between the peak target current and the morphology of chromium nitride thin films deposited by reactive high power pulsed magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. D 42, 015304 (2009).
J.T. Gudmundsson, P. Sigurjonsson, P. Larsson, D. Lundin, and U. Helmersson: On the electron energy in the high power impulse magnetron sputtering discharge. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 123302 (2009).
J. Bohlmark, J.T. Gudmundsson, J. Alami, M. Lattemann, and U. Helmersson: Spatial electron density distribution in a high-power pulsed magnetron discharge. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 33, 346 (2005).
J.T. Gudmundsson: The high power impulse magnetron sputtering discharge as an ionized physical vapor deposition tool. Vacuum 84, 1360 (2010).
J. Vlcek, P. Kudlacek, K. Burcalova, and J. Musil: Ion flux characteristics in high-power pulsed magnetron sputtering discharges. Europhys. Lett. 77, 45002 (2007).
J. Bohlmark, J. Alami, C. Christou, A.P. Ehiasarian, and U. Helmersson: Ionization of sputtered metals in high power pulsed magnetron sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 23, 18 (2005).
K. Macák, V. Kouznetsov, J. Schneider, U. Helmersson, and I. Petrov: Ionized sputter deposition using an extremely high plasma density pulsed magnetron discharge. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 18, 1533 (2000).
B.M. DeKoven, P.R. Ward, R.E. Weiss, D.J. Christie, R.A. Scholl, W.D. Sproul, F. Tomasel, and A. Anders: Carbon thin film deposition using high power pulsed magnetron sputtering, in Society of Vacuum Coaters 46th Annual Technical Conference Proceedings, May 3–8 (San Francisco, CA, 2003), p. 158.
J.A. Hopwood: Plasma Physics. Thin Films: Ionized Physical Vapor Deposition, edited by J.A. Hopwood (Academic Press, San Diego, 2000).
S.M. Rossnagel and J. Hopwood: Magnetron sputter deposition with high levels of metal ionization. Appl. Phys. Lett. 63, 3285 (1993).
J. Vlcek, P. Kudlacek, K. Burcalova, and J. Musil: High-power pulsed sputtering using a magnetron with enhanced plasma confinement. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 25, 42 (2007).
K. Burcalova, A. Hecimovic, and A.P. Ehiasarian: Ion-energy distributions and efficiency of sputtering process in HIPIMS system. J. Phys. D 41, 115306 (2008).
A. Anders, J. Andersson, and A. Ehiasarian: High power impulse magnetron sputtering: Current-voltage-time characteristics indicate the onset of sustained self-sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 102, 113303 (2007).
J. Andersson, A.P. Ehiasarian, and A. Anders: Observation of Ti4+ ions in a high power impulse magnetron sputtering plasma. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 071504 (2008).
J. Rosén, A. Anders, S. Mráz, and J.M. Schneider: Charge-state-resolved ion energy distributions of aluminum vacuum arcs in the absence and presence of a magnetic field. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 103306 (2005).
A. Anders: Self-sputtering runaway in high power impulse magnetron sputtering: The role of secondary electrons and multiply charged metal ions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 201501 (2008).
J. Andersson and A. Anders: Gasless sputtering: Opportunities for ultraclean metallization, coatings in space, and propulsion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 221503 (2008).
L.I. Wei, M.A. Zhong-Quan, W. Ye, and W. De-Ming: Optimization of energy scope for titanium nitride films grown by ion beam-assisted deposition. Chin. Phys. Lett. 23, 178 (2006).
D. Lundin, P. Larsson, E. Wallin, M. Lattemann, N. Brenning, and U. Helmersson: Cross-field ion transport during high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 17, 035021 (2008).
F. Eriksson, N. Ghafoor, F. Schäfers, E.M. Gullikson, and J. Birch: Interface engineering of short-period Ni/V multilayer x-ray mirrors. Thin Solid Films 500, 84 (2006).
A. Hecimovic and A.P. Ehiasarian: Time evolution of ion energies in HIPIMS of chromium plasma discharge. J. Phys. D 42, 135209 (2009).
A. Hecimovic and A.P. Ehiasarian: Temporal evolution of the ion fluxes for various elements in HIPIMS plasma discharge. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 39, 1154 (2011).
W.P. Leroy, S. Konstantinidis, S. Mahieu, R. Snyders, and D. Depla: Angular-resolved energy flux measurements of a dc- and HIPIMS-powered rotating cylindrical magnetron in reactive and non-reactive atmosphere. J. Phys. D 44, 115201 (2011).
D. Lundin, M. Stahl, H. Kersten, and U. Helmersson: Energy flux measurements in high power impulse magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. D 42, 185202 (2009).
G. West, P. Kelly, P. Barker, A. Mishra, and J. Bradley: Measurements of deposition rate and substrate heating in a HiPIMS discharge. Plasma Processes Polym. 6, S543 (2009).
D.W. Hoffman: A sputtering wind. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 3, 561 (1985).
S.M. Rossnagel: Gas density reduction effects in magnetrons. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 6, 19 (1988).
A. Palmero, H. Rudolph, and F.H.P.M. Habraken: Gas heating in plasma-assisted sputter deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 071501 (2005).
A. Palmero, H. Rudolph, and F.H.P.M. Habraken: Study of the gas rarefaction phenomenon in a magnetron sputtering system. Thin Solid Films 515, 631 (2006).
I. Kolev and A. Bogaerts: Calculation of gas heating in a dc sputter magnetron. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 093301 (2008).
S. Kadlec: Simulation of neutral particle flow during high power magnetron impulse. Plasma Processes Polym. 4, S419 (2007).
U. Helmersson, M. Lattemann, J. Alami, J. Bohlmark, A.P. Ehiasarian, and J.T. Gudmundsson: High power impulse magnetron sputtering discharges and thin film growth: A brief review, in Society of Vacuum Coaters 48th Annual Technical Conference Proceedings, April 23–28 (Denver, CO, 2005), p. 458.
D.J. Christie: Target material pathways model for high power pulsed magnetron sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 23, 330 (2005).
P. Poolcharuansin and J.W. Bradley: Short- and long-term plasma phenomena in a HiPIMS discharge. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 19, 025010 (2010).
S. Konstantinidis, J.P. Dauchot, M. Ganciu, and M. Hecq: Transport of ionized metal atoms in high-power pulsed magnetron discharges assisted by inductively coupled plasma. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 021501 (2006).
S.P. Bugaev, N.N. Koval, N.S. Sochugov, and A.N. Zakharov: Investigation of a high-current pulsed magnetron discharge initiated in the low-pressure diffuse arc plasma, in Proceedings of the XVIIth International Symposium on Discharges and Electrical Insulation in Vacuum, July 21–26 (Berkeley, CA, 1996), p. 1074.
J. Bohlmark, M. Östbye, M. Lattemann, H. Ljungcrantz, T. Rosell, and U. Helmersson: Guiding the deposition flux in an ionized magnetron discharge. Thin Solid Films 515, 1928 (2006).
A. Mishra, P.J. Kelly, and J.W. Bradley: The evolution of the plasma potential in a HiPIMS discharge and its relationship to deposition rate. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 19, 045014 (2010).
J. Emmerlich, S. Mráz, R. Snyders, K. Jiang, and J.M. Schneider: The physical reason for the apparently low deposition rate during high power pulsed magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 82, 867 (2008).
N. Brenning, R.L. Merlino, D. Lundin, M.A. Raadu, and U. Helmersson: Faster-than-Bohm Cross-B Electron Transport in Strongly Pulsed Plasmas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 225003 (2009).
D. Lundin, U. Helmersson, S. Kirkpatrick, S. Rohde, and N. Brenning: Anomalous electron transport in high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 17, 025007 (2008).
N. Brenning, C. Huo, D. Lundin, M.A. Raadu, C. Vitelaru, G.D. Stancu, T. Minea, and U. Helmersson: Understanding deposition rate loss in high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. (2011, in press).
M. Aiempanakit, T. Kubart, P. Larssron, K. Sarakinos, J. Jensen, and U. Helmersson: Hysteresis and process stability in reactive high power impulse magnetron sputtering of metal oxides. Thin Solid Films 519, 7779 (2011).
J. Lazar, J. Vlcek, and J. Rezek: Ion flux characteristics and efficiency of the deposition processes in high power impulse magnetron sputtering of zirconium. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 063307 (2010).
D. Horwat and A. Anders: Compression and strong rarefaction in high power impulse magnetron sputtering discharges. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 123306 (2010).
J. Lin, J.J. Moore, W.D. Sproul, B. Mishra, J.A. Rees, Z. Wu, R. Chistyakov, and B. Abraham: Ion energy and mass distributions of the plasma during modulated pulse power magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Tech. 203, 3676 (2009).
L. Meng, A.N. Cloud, S. Jung, and D.N. Ruzic: Study of plasma dynamics in a modulated pulsed power magnetron discharge using a time-resolved Langmuir probe. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 29, 011024 (2011).
M. Hála, J. Capek, O. Zabeida, J.E. Klemberg-Sapieha, and L. Martinu: Pulse management in high power pulsed magnetron sputtering process: I. Effect on the characteristics of Ar discharge and Nb coatings. J. Phys. D (2011, in press).
A.E. Ross, R. Sangines, B. Treverrow, M.M.M. Bilek, and D.R. McKenzie: Optimizing efficiency of Ti ionized deposition in HIPIMS. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 20, 035021 (2011).
S. Berg and T. Nyberg: Fundamental understanding and modeling of reactive sputtering processes. Thin Solid Films 476, 215 (2005).
D. Depla and R. De Gryse: Target poisoning during reactive magnetron sputtering: Part I: The influence of ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Tech. 183, 184 (2004).
D. Severin, O. Kappertz, T. Kubart, T. Nyberg, S. Berg, A. Pflug, M. Siemers, and M. Wuttig: Process stabilization and increase of the deposition rate in reactive sputtering of metal oxides and oxynitrides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 161504 (2006).
W.D. Sproul, M.E. Graham, M.S. Wong, S. Lopez, D. Li, and R.A. Scholl: Reactive direct current magnetron sputtering of aluminum oxide coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 13, 1188 (1995).
K. Sarakinos, J. Alami, C. Klever, and M. Wuttig: Process stabilization and enhancement of deposition rate during reactive high power pulsed magnetron sputtering of zirconium oxide. Surf. Coat. Tech. 202, 5033 (2008).
D. Depla and R. De Gryse: Cross section for removing chemisorbed oxygen from an aluminum target by sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 20, 521 (2002).
B. Clarenbach, B. Lorenz, M. Krämer, and N. Sadeghi: Time-dependent gas density and temperature measurements in pulsed helicon discharges in argon. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 12, 345 (2003).
K. Sarakinos, J. Alami, and M. Wuttig: Process characteristics and film properties upon growth of TiOx films by high power pulsed magnetron sputtering. J Phys. D 40, 2108 (2008).
T. Kubart, M. Aiempanakit, J. Andersson, T. Nyberg, S. Berg, and U. Helmersson: Studies of hysteresis effect in reactive HiPIMS deposition of oxides. Surf. Coat. Tech. 205, S303 (2011).
D.M. Mattox: Handbook of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Processing (Noyes Publications, Westwood, 1998).
O. Auciello and R. Kelly: Ion Bombardment Modification of Surfaces: Fundamentals and Applications (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1984).
I. Petrov, P.B. Barna, L. Hultman, and J.E. Greene: Microstructural evolution during film growth. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 21, S117 (2003).
J. Dalla Torre, G.H. Gilmer, D.L. Windt, R. Kalyanaraman, F.H. Baumann, P.L. O’Sullivan, J. Sapjeta, T. Díaz de la Rubia, and M. Djafari Rouhani: Microstructure of thin tantalum films sputtered onto inclined substrates: Experiments and atomistic simulations. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 263 (2003).
W. Ensiger: Low energy ion assist during deposition—an effective tool for controlling thin film microstructure. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 127–, 796 (1997).
C.R. Tellier and A.J. Tosser: Size Effects in Thin Films (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1982).
R.C. Munoz, R. Finger, C. Arenas, G. Kremer, and L. Moraga: Surface-induced resistivity of thin metallic films bounded by a rough fractal surface. Phys. Rev. B 66, 205401 (2002).
H. Weis, T. Müggenburg, P. Grosse, L. Herlitze, I. Friedrich, and M. Wuttig: Advanced characterization tools for thin films in low-E systems. Thin Solid Films. 351, 184 (1999).
P. Siemroth and T. Schülke: Copper metallization in microelectronics using filtered vacuum arc deposition—principles and technological development. Surf. Coat. Tech. 133–, 106 (2000).
J. Alami, S. Bolz, and K. Sarakinos: High power pulsed magnetron sputtering: Fundamentals and applications. J. Alloy. Comp. 483, 530 (2009).
T. Schuelke, T. Witke, H.J. Scheibe, P. Siemroth, B. Schultrich, O. Zimmer, and J. Vetter: Comparison of DC and AC arc thin film deposition techniques. Surf. Coat. Tech. 120–, 226 (1999).
R. Berisch: Sputtering by Particle Bombardment I (Springer, Berlin, 1982).
R. Chistyakov, B. Abraham, W.D. Sproul, J. Moore, and J. Lin: Modulated pulse power technology and deposition for protective and tribological coatings, in Society of Vacuum Coaters 50th Annual Technical Conference Proceedings, April 28–May 3 (Louisville, KY, 2007), p. 139.
T. Michely and J. Krug: Islands Mounts and Atoms (Springer, Berlin, 2004).
I. Petrov, F. Adibi, J.E. Greene, L. Hultman, and J.E. Sundgren: Average energy deposited per atom: A universal parameter for describing ion-assisted film growth? Appl. Phys. Lett. 63, 36 (1993).
G.C.A.M. Janssen and J.D. Kamminga: Stress in hard metal films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 3086 (2004).
Y. Pauleau: Generation and evolution of residual stresses in physical vapour-deposited thin films. Vacuum 61, 175 (2001).
H. Windischmann: Intrinsic stress in sputter-deposited thin-films. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 17, 547 (1992).
C.A. Davis: A simple model for the formation of compressive stress in thin films by ion bombardment. Thin Solid Films 226, 30 (1993).
L.A. Clevenger, A. Mutscheller, J.M.E. Harper, C. Cabral, and K. Barmak: The relationship between deposition conditions, the beta to alpha phase transformation, and stress relaxation in tantalum thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 72, 4918 (1992).
D.W. Face and D.E. Prober: Nucleation of body-centered-cubic tantalum films with a thin niobium underlayer. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 5, 3408 (1987).
J. Alami, P. Eklund, J. Emmerlich, O. Wilhelmsson, U. Jansson, H. Högberg, L. Hultman, and U. Helmersson: High-power impulse magnetron sputtering of Ti–Si–C thin films from a Ti3SiC2 compound target. Thin Solid Films 515, 1731 (2006).
M.W. Barsoum: TheMn+1AXn Phases: A new class of solids, thermodynamically stable nanolaminates. Prog. Solid State Chem. 28, 201 (2000).
P. Eklund, M. Beckers, U. Jansson, H. Högberg, and L. Hultman: The Mn+1AXn phases: Materials science and thin-film processing. Thin Solid Films 518, 1851 (2010).
J. Alami, K. Sarakinos, F. Uslu, C. Klever, J. Dukwen, and M. Wuttig: On the phase formation of titanium oxide films grown by reactive high power pulsed magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. D 42, 115204 (2009).
V. Stranak, M. Quaas, H. Wulff, Z. Hubicka, S. Wrehde, M. Tichy, and R. Hippler: Formation of TiOx films produced by high-power pulsed magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. D 41, 055202 (2008).
M. Aiempanakit, U. Helmersson, A. Aijaz, P. Larsson, R. Magnusson, J. Jensen, and T. Kubart: Effect of peak power in reactive high power impulse magnetron sputtering of titanium dioxide. Surf. Coat. Tech. 205, 4828 (2011).
R. Bandorf, M. Vergöhl, P. Giesel, T. Wallendorf, and G. Mark: Investigation of HPPMS titania thin films prepared by unipolar, DC-superimposed and bipolar sputtering, in Society of Vacuum Coaters 50th Annual Technical Conference Proceedings, April 28–May 3 (Louisville, KY, 2007), p. 160.
M.D. Wiggins, M.C. Nelson, and C.R. Aita: Phase development in sputter deposited titanium dioxide. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 14, 772 (1996).
W. Zhou, X.X. Zhong, X.C. Wu, L.Q. Yuan, Q.W. Shu, W. Li, and Y.X. Xia: Low-temperature deposition of nanocrystalline TiO2 films: Enhancement of nanocrystal formation by energetic particle bombardment. J. Phys D 40, 219 (2007).
P.B. Barna and M. Adamik: Fundamental structure forming phenomena of polycrystalline films and the structure zone models. Thin Solid Films 317, 27 (1998).
J.S. Koehler: Attempt to design a strong solid. Phys. Rev. B 2, 547 (1970).
P.M. van Attekum, P.H. Woerlee, G.C. Verkade, and A.A. Hoeben: Influence of grain boundaries and surface Debye temperature on the electrical resistance of thin gold films. Phys. Rev. B 29, 645 (1984).
A. Anders: A structure zone diagram including plasma-based deposition and ion etching. Thin Solid Films 518, 4087 (2010).
G. Greczynski, J. Jensen, J. Böhlmark, and L. Hultman: Microstructure control of CrNx films during high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Tech. 205, 118 (2010).
A.P. Ehiasarian, P.E. Hovsepian, L. Hultman, and U. Helmersson: Comparison of microstructure and mechanical properties of chromium nitride-based coatings deposited by high power impulse magnetron sputtering and by the combined steered cathodic arc/unbalanced magnetron technique. Thin Solid Films 457, 270 (2004).
A.P. Ehiasarian, W-D. Münz, L. Hultman, U. Helmersson, and I. Petrov: High power pulsed magnetron sputtered CrNx films. Surf. Coat. Tech. 163–, 267 (2003).
J. Vetter, T. Michler, and H. Steuernagel: Hard coatings on thermochemically pretreated soft steels: Application potential for ball valves. Surf. Coat. Tech. 111, 210 (1999).
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. Ante Hecimovic for valuable input. One of the authors (K. Sarakinos) acknowledges the Swedish Research Council (VR) for the financial support through the postdoctoral project 623-2009-7348.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lundin, D., Sarakinos, K. An introduction to thin film processing using high-power impulse magnetron sputtering. Journal of Materials Research 27, 780–792 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.8