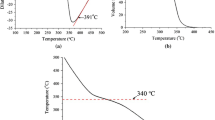
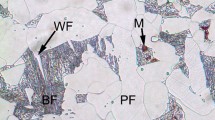
Abstract
Nanoindentation experiments and microstructural analysis were performed on advanced 12% Cr ferritic steel having extremely fine and complex martensitic microstructures, to answer unsolved questions on the contributions of grain boundaries to strengthening and aging degradation mechanisms in both as-tempered and thermally aged steels. Interesting features of the experimental results led us to suggest that among several high angle boundaries, block boundary is most effective in enhancing the macroscopic strength in as-tempered virgin sample, and that a decrease in matrix strength rather than reduction in grain-boundary strengthening effect is primarily responsible for the macroscopic softening behavior observed during thermal exposure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.L. Klueh: Elevated temperature ferritic and martensitic steels and their application to future nuclear reactors. Int. Mater. Rev. 50, 287 (2005).
G. Krauss: Martensite in steel: Strength and structure. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 273–275, 40 (1999).
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy (McGraw-Hill, UK, 1988) p. 184.
J.M. Marder and A.R. Marder: The morphology of iron-nickel massive martensite. Trans. ASM 62, 1 (1969).
T. Maki, K. Tsuzaki, and I. Tamura: The morphology of microstructure composed of lath martensites in steels. Trans. ISIJ 20, 207 (1980).
J.W. Morris Jr., Z. Guo, C.R. Krenn, and Y.H. Kim: The limits of strength and toughness in steel. ISIJ Int. 41, 599 (2001).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 19, 3 (2004).
T. Ohmura, K. Tsuzaki, and S. Matsuoka: Nanohardness measurement of high-purity Fe-C martensite. Scripta Mater. 45, 889 (2001).
T. Ohmura, T. Hara, and K. Tsuzaki: Relationship between nanohardness and microstructures in high-purity Fe-C as-quenched and quench-tempered martensite. J. Mater. Res. 18, 1465 (2003).
T. Ohmura, T. Hara, and K. Tsuzaki: Evaluation of temper softening behavior of Fe-C binary martensitic steels by nanoindentation. Scripta Mater. 49, 1157 (2003).
J. Li, T. Ohmura, and K. Tzsuzaki: Evaluation of grain boundary effect on strength of Fe-C low alloy martensitic steels by nanoindentation technique. Mater. Trans. 46, 1301 (2005).
K. Sawada, K. Miyahara, H. Kushima, K. Kimura, and S. Matsuoka: Contribution of microstructural factors to hardness change during creep exposure in mod. 9Cr-1Mo steel. ISIJ Int. 45, 1934 (2005).
F. Masuyama and N. Komai: Long-term creep rupture strength of tungsten-strengthened advanced 9–12% Cr steels. Key Eng. Mater. 171–174, 179 (2000).
S. Komazaki, T. Hashida, T. Shoji, and K. Suzuki: Development of small punch tests for creep property measurement of tungsten-alloyed 9% Cr ferritic steels. J. Test. Eval. 28, 249 (2000).
H. Kutsumi, A. Chino, and Y. Ishibashi: Quantitative analysis of laves phase and carbide in high Cr heat-resistance ferritic steels. Tetsu to Hagane 78, 5941992 in Japanese.
R. Ishii, Y. Tsuda, K. Fujiyama, K. Kimura, and K. Saito: Creep damage estimation based on the softening behavior of 10Cr-1Mo-1W-VNbN steel. Tetsu to Hagane 89, 6992003 in Japanese.
K. Sawada, M. Takeda, K. Maruyama, R. Ishii, M. Yamada, Y. Nagae, and R. Komine: Effect of W on recovery of lath structure during creep of high chromium martensite steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 267, 19 (1999).
M. Kimura, K. Yamaguchi, M. Hayakawa, and K. Kobayashi: Microstructure and grain boundary precipitates in 9-12% Cr ferritic heat-resisting steels. Tetsu to Hagane 90, 272004 in Japanese.
W.D. Nix and H. Gao: Indentation size effects in crystalline materials: A law for strain gradient plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 46, 411 (1998).
H. Gao and Y. Huang: Geometrically necessary dislocation and size-dependent plasticity. Scripta Mater. 48, 113 (2003).
K.L. Johnson: The correlation of indentation experiments. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 18, 115 (1970).
M. Yamada, O. Watanabe, Y. Yoshioka, and M. Miyazaki: Development of advanced 12Cr steel rotor forgings. Tetsu to Hagane 76, 10841990 in Japanese.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, J., Shim, S., Komazaki, S. et al. A nanoindentation study on grain-boundary contributions to strengthening and aging degradation mechanisms in advanced 12 Cr ferritic steel. Journal of Materials Research 22, 175–185 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2007.0009
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2007.0009