Article contents
Optical properties of high-quality nanohole arrays in gold made using soft-nanoimprint lithography
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 November 2015
Abstract
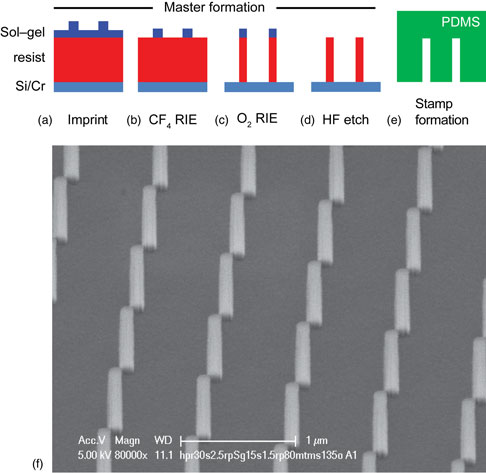
We present a novel soft-nanoimprint procedure to fabricate high-quality sub-wavelength hole arrays in optically thick films of gold on glass substrates. We fabricate 0.5 × 0.5 mm2 structures composed of a square array of 180 nm-diameter holes with a 780 nm pitch. Optical angular transmission measurements on the arrays show clear extraordinary transmission peaks corresponding to the dispersion of surface plasmon polaritons propagating on either side of the metal film. The transmission features can be strongly controlled by engineering the dielectric environment around the holes. As the nanoimprint procedure enables fabrication of nanoscale patterns over wafer-scale areas at low cost, these imprinted metal nanoparticle arrays can find applications in, e.g., optical components, photovoltaics, integrated optics, and microfluidics.
- Type
- Plasmonics, Photonics, and Metamaterials Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2015
References
- 6
- Cited by




