Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Lin, Yu-Chun
Jansohn, Peter
and
Boulouchos, Konstantinos
2014.
Turbulent flame speed for hydrogen-rich fuel gases at gas turbine relevant conditions.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,
Vol. 39,
Issue. 35,
p.
20242.
Savard, Bruno
and
Blanquart, Guillaume
2014.
An a priori model for the effective species Lewis numbers in premixed turbulent flames.
Combustion and Flame,
Vol. 161,
Issue. 6,
p.
1547.
Sahu, A.B.
and
Ravikrishna, R.V.
2014.
A detailed numerical study of NOx kinetics in low calorific value H2/CO syngas flames.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,
Vol. 39,
Issue. 30,
p.
17358.
Mantzaras, John
2014.
Modeling and Simulation of Heterogeneous Catalytic Processes.
Vol. 45,
Issue. ,
p.
97.
Kheirkhah, Sina
and
Gülder, Ömer L.
2015.
Consumption speed and burning velocity in counter-gradient and gradient diffusion regimes of turbulent premixed combustion.
Combustion and Flame,
Vol. 162,
Issue. 4,
p.
1422.
Tamadonfar, Parsa
and
Gülder, Ömer L.
2015.
Effects of mixture composition and turbulence intensity on flame front structure and burning velocities of premixed turbulent hydrocarbon/air Bunsen flames.
Combustion and Flame,
Vol. 162,
Issue. 12,
p.
4417.
Yasari, E.
Verma, S.
and
Lipatnikov, A. N.
2015.
RANS Simulations of Statistically Stationary Premixed Turbulent Combustion Using Flame Speed Closure Model.
Flow, Turbulence and Combustion,
Vol. 94,
Issue. 2,
p.
381.
Savard, Bruno
and
Blanquart, Guillaume
2015.
Broken reaction zone and differential diffusion effects in high Karlovitz n-C7H16 premixed turbulent flames.
Combustion and Flame,
Vol. 162,
Issue. 5,
p.
2020.
Fragner, Romain
Halter, Fabien
Mazellier, Nicolas
Chauveau, Christian
and
Gökalp, Iskender
2015.
Investigation of pressure effects on the small scale wrinkling of turbulent premixed Bunsen flames.
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 2,
p.
1527.
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
Chomiak, Jerzy
Sabelnikov, Vladimir A.
Nishiki, Shinnosuke
and
Hasegawa, Tatsuya
2015.
Unburned mixture fingers in premixed turbulent flames.
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 2,
p.
1401.
Brambilla, Andrea
Schultze, Marco
Frouzakis, Christos E.
Mantzaras, John
Bombach, Rolf
and
Boulouchos, Konstantinos
2015.
An experimental and numerical investigation of premixed syngas combustion dynamics in mesoscale channels with controlled wall temperature profiles.
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 3,
p.
3429.
Fogla, Navin
Creta, Francesco
and
Matalon, Moshe
2015.
Effect of folds and pockets on the topology and propagation of premixed turbulent flames.
Combustion and Flame,
Vol. 162,
Issue. 7,
p.
2758.
Zhang, Meng
Wang, Jinhua
Jin, Wu
Huang, Zuohua
Kobayashi, Hideaki
and
Ma, Lin
2015.
Estimation of 3D flame surface density and global fuel consumption rate from 2D PLIF images of turbulent premixed flame.
Combustion and Flame,
Vol. 162,
Issue. 5,
p.
2087.
Verma, Salman
and
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
2016.
Does sensitivity of measured scaling exponents for turbulent burning velocity to flame configuration prove lack of generality of notion of turbulent burning velocity?.
Combustion and Flame,
Vol. 173,
Issue. ,
p.
77.
Thiesset, F.
Maurice, G.
Halter, F.
Mazellier, N.
Chauveau, C.
and
Gökalp, I.
2016.
Geometrical properties of turbulent premixed flames and other corrugated interfaces.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 93,
Issue. 1,
Fogla, N.
Creta, F.
and
Matalon, M.
2017.
The turbulent flame speed for low-to-moderate turbulence intensities: Hydrodynamic theory vs. experiments.
Combustion and Flame,
Vol. 175,
Issue. ,
p.
155.
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
Chomiak, Jerzy
Sabelnikov, Vladimir A.
Nishiki, Shinnosuke
and
Hasegawa, Tatsuya
2018.
A DNS study of the physical mechanisms associated with density ratio influence on turbulent burning velocity in premixed flames.
Combustion Theory and Modelling,
Vol. 22,
Issue. 1,
p.
131.
Alvarez-Socorro, A. J.
Clerc, Marcel G.
Ferré, M. A.
and
Knobloch, Edgar
2019.
Front depinning by deterministic and stochastic fluctuations: A comparison.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 99,
Issue. 6,
Chen, Yangyang
Liu, Aodong
Deng, Banglin
Xu, Zhenxin
Feng, Renhua
Fu, Jianqin
Liu, Xiaoqiang
Zhang, Guoqing
and
Zhou, Lili
2019.
The influences of ignition modes on the performances for a motorcycle single cylinder gasoline engine at lean burn operation: Looking inside interaction between flame front and turbulence.
Energy,
Vol. 179,
Issue. ,
p.
528.
Schulz, Oliver
and
Noiray, Nicolas
2019.
Combustion regimes in sequential combustors: Flame propagation and autoignition at elevated temperature and pressure.
Combustion and Flame,
Vol. 205,
Issue. ,
p.
253.
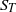 ${S}_{T} $) and mean flamelets speeds (stretched laminar flame speeds,
${S}_{T} $) and mean flamelets speeds (stretched laminar flame speeds, 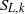 ${S}_{L, k} $). Fuels with significantly different thermodiffusive properties have been investigated, ranging from pure methane to syngas (
${S}_{L, k} $). Fuels with significantly different thermodiffusive properties have been investigated, ranging from pure methane to syngas (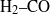 ${\mathrm{H} }_{2} \text{{\ndash}} \mathrm{CO} $ blends) and pure hydrogen, while the pressure was varied from 0.1 to 1.25 MPa. Flame front corrugation was measured with planar laser-induced fluorescence (PLIF) of the OH radical, while turbulence quantities were determined with particle image velocimetry (PIV). Two different analyses based on mass balance were performed on the acquired flame images. The first method assessed absolute values of turbulent flame speeds and the second method, by means of an improved fractal methodology, provided normalized turbulent flame speeds (
${\mathrm{H} }_{2} \text{{\ndash}} \mathrm{CO} $ blends) and pure hydrogen, while the pressure was varied from 0.1 to 1.25 MPa. Flame front corrugation was measured with planar laser-induced fluorescence (PLIF) of the OH radical, while turbulence quantities were determined with particle image velocimetry (PIV). Two different analyses based on mass balance were performed on the acquired flame images. The first method assessed absolute values of turbulent flame speeds and the second method, by means of an improved fractal methodology, provided normalized turbulent flame speeds (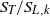 ${S}_{T} / {S}_{L, k} $). Deduced average Markstein numbers exhibited a strong dependence on pressure and hydrogen content of the reactive mixture. It was shown that preferential-diffusive-thermal (PDT) effects acted primarily on enhancing the stretched laminar flame speeds rather than on increasing the flame front corrugations. Interaction between flame front and turbulent eddies measured by the fractal dimension was shown to correlate with the eddy temporal activity.
${S}_{T} / {S}_{L, k} $). Deduced average Markstein numbers exhibited a strong dependence on pressure and hydrogen content of the reactive mixture. It was shown that preferential-diffusive-thermal (PDT) effects acted primarily on enhancing the stretched laminar flame speeds rather than on increasing the flame front corrugations. Interaction between flame front and turbulent eddies measured by the fractal dimension was shown to correlate with the eddy temporal activity.



