Early identification and monitoring of new and emerging health technologies has been of interest in health technology assessment (HTA) agencies for many years (12–Reference Oortwijn, Vondeling and Bouter14). The agencies involved have developed programs under different synonyms, for example, horizon scanning, early warning, emerging technology assessment, alert, and early awareness and alert systems (EAASs). In 1998, EuroScan (international information network on new and emerging health technologies), a collaborative network of international (not only European, 19 agencies in 2008) agencies conducting horizon scanning, was founded (Reference Carlsson and Jørgensen2;7). Some agencies publish outputs as short (4–6 pages) reports—Technology Briefings (National Horizon Scanning Centre, England), TechNotes (former Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research, Canada), Alerts (Swedish Council on Technology Assessment in Health Care, Sweden), Emerging Technology Bulletins (Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health, Canada)—on their respective Web sites and actively distribute them to a small number of regional and national decision makers.
Western healthcare systems are confronted with a rising number of new technologies. In globalized markets, many of these systems must make decisions on the managed introduction or reimbursement of the same technologies. Work Package 7 (WP7) of the European network for Health Technology Assessment (EUnetHTA) (Reference Kristensen, Lampe and Chase10;Reference Kristensen, Mäkelä and Allgurin Neikter11) aimed to contribute toward avoiding duplication by making the information gathered in formal horizon scanning activities available to a wider audience. WP7 would do this by “disseminating information on early identification and assessment activities” (Reference Wild and Langer17) beyond regional or national decision makers and to countries within the European Union (EU) that had not established systems for identifying new and emerging health technologies. This idea is not new. Conclusions from a workshop (Scanning the Horizon for Emerging Health Technology) in 1997 strongly recommended that agencies working with early warning should collaborate and coordinate, with a primary focus on sharing information at different levels (Reference Carlsson and Jørgensen2). Wider dissemination of information on new and emerging technologies was revisited in 2001 by the European Collaboration for Health Technology Assessment/ Assessment of Health Interventions (ECHTA/ECAHI) project, funded by the European Commission (Reference Hagenfeldt, Asua and Bellucci9). Consolidation of the pilot, electronic EuroScan database was recommended, with access being limited to EuroScan members in the short to medium term. In 2005 (Reference Packer and Simpson15), a status report from EuroScan listed potential projects, for example, a newsletter or digest for nonmembers, producing reports with a shared focus, and widening nonmember access to the early warning database. The “core early assessment” idea was also raised, further indicating the potential for more exchange of information relative to the current situation.
AIMS AND OBJECTIVE
The task of EUnetHTA Work Package 7, Strand B (WP7B) was to develop a European-wide newsletter on new and emerging health technologies and to provide information on costly, high-volume, rapidly developing technologies that could significantly impact health care. This newsletter should contain information on the technology itself, on the nature of the condition (burden of disease), on the prevalence of the disease, and on standard treatments and their effectiveness. Because this newsletter would be highly visible and could potentially impact on setting the agenda and discussing new and emerging technologies throughout Europe, the underlying processes of its production were required to be transparent and reproducible. This particularly applied to the methods used in selecting the technologies to be included in the newsletter.
This article: (i) describes the general principles for identifying, filtering, and prioritizing new and emerging health technologies; (ii) describes the process and method underlying how the EuroScan database was used to develop a newsletter and how an international panel selected technologies from this database for the newsletter; and (iii) discusses issues related to future priority setting exercises, information sharing in this field, and methodological issues concerning the choices made.
STRUCTURE AND METHODS
General Principles for Identification and Priority Setting
The horizon scanning process aims to inform about developing technologies that may significantly impact health care. Briefly, the process consists of five sequenced, main components (Reference Packer and Simpson15): (i) Identification, (ii) prioritization, (iii) early assessment and impact prediction, (iv) dissemination, and (v) monitoring. To report on selecting topics for the information service (newsletter) and making this process reproducible and transparent, we describe only the first two steps (identification and prioritization) in greater detail.
Identification. The challenge of identifying new health technologies involves gathering information of sufficient quality from a huge quantity of data (Reference Douw, Vondeling, Eskildsen and Simpson4). Many scientific developments appear on the horizon, but never reach the market stage. Others can, seemingly from nowhere, diffuse rapidly throughout the healthcare system. Hence, identification may be perceived as the first part of filtering before the prioritization process.
Depending on the field of interest a broad spectrum of identification sources must be selected and scanned regularly. Some horizon scanning programs focus only on specific medical fields or technology types (e.g., ASERNIP-S/Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures-Surgical; LBI-HTA/Ludwig Boltzmann Institute of Health Technology Assessment: Oncology (Reference Geiger-Gritsch8)), whereas others address the whole range of technologies and specialties (NHSC, CADTH). To overview different identification procedures we must recognize that the diffusion contexts for health technologies differ considerably. Some technologies must pass regulatory hurdles, resulting in more predictable market entry, for example, drugs that must be approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMEA). Others, for example, surgical procedures, generally emerge within medical professions in more random manner without formal market approval. Similarly the speed of diffusion varies, with pharmaceuticals generally diffusing more rapidly than devices (Reference Booth-Clibborn, Packer and Stevens1). Given these different diffusion conditions, one can assume that information sources will vary by technology type.
A classification of health technologies (Reference Robert, Stevens and Gabbay16) aims to explore the most useful sources for identifying new ones. Monitoring the sectors where technologies are most likely to originate, dozens of specific sources are scanned regularly for the following: Pharmaceuticals, Diagnostic strategies, Procedures, Procedural devices, Other medical and assistive devices, Healthcare settings or treatment delivery systems, Information technology, and New professions.
Attempts to classify the huge number of sources offering information on health technologies involve (most common) categorization into primary, secondary, and tertiary sources. Primary sources provide information from developers or manufacturers, for example, patents, FDA licensing applications, and company Web sites. Secondary sources provide information (mostly published) on the technology in use from medical, financial, or social perspectives, for example, drug information services, conference abstracts, journals, expert groups, etc. Tertiary sources provide information from other organizations engaged in identifying new healthcare technologies, for example, other horizon scanning products. The separation into primary, secondary, and tertiary also highlights trade-offs between earlier “warning” (timeliness), volume, and greater accuracy of the information provided. For example, the Austrian program scans sixty-three sources regularly/weekly, solely to identify drugs in oncology (Reference Geiger-Gritsch8). In other fields (e.g., telemedicine or cardiology devices) fewer sources might be scanned less frequently.
Priority Setting. Identification reveals many of the health technologies that appear on the horizon. The next step is to select the technologies in which to invest further resources (Reference Douw, Vondeling and Oortwijn5). The general objective of priority setting in horizon scanning is to define the potentially most significant new and emerging technologies in which to invest scarce assessment resources. Obviously, the term “most significant” is ambiguous and requires further definition in terms of impact on patients, health service, and/or costs. Generally, in this stage of horizon scanning a choice will be made whether to assess a technology or continue to monitor it.
Because the process of selecting technologies by agreement (Reference Douw and Vondeling3) is susceptible to subjectivity, some tools capable of enhancing accountability in the selection process have been developed for the EU information service on emerging technologies. In addition to using explicit criteria, it will be necessary to define individual criteria to improve common understanding. Another tool is a formal checklist of the selection criteria and their indicators to assure that all criteria receive equal consideration. Finally, documentation of the decision-making process substantially enhances accountability and transparency.
EuroScan member agencies identify and prioritize new and emerging health technologies as described. Members add the health technologies they identify and prioritize to the EuroScan database of new and emerging health technologies and continuously update the Web-based database, adding around 200 new entries annually (6).
Developing an EU-wide Newsletter
The EUnetHTA newsletter on high-volume, costly, and rapidly developing new and emerging health technologies aimed to provide information on the technologies’ early stage of development and on their possible significant impact on health care in the EU. Information in the newsletter was intended to help decision makers better anticipate, plan, and manage the introduction and diffusion of new health technologies. It was proposed that the newsletter would be published quarterly, and that each issue would cover eight to twelve technologies, providing information of various depth and detail, depending on the results of scoring the potential significance and impact of the respective health technology: One type 1 technology, 3 to 4 type 2 technologies, and 4 to 7 type 3 technologies (Box 1).
Box 1. Types of Articles Providing Different Depths of Information

To be objective and transparent about the contents of the newsletter, a method for prioritizing health technologies was imperative. The EuroScan secretariat at the National Horizon Scanning Centre (NHSC) in England was actively involved in planning and developing methods for the production of the newsletter. All EuroScan members agreed that EuroScan's database of new and emerging technologies could be used as a source of information on pertinent technologies.
Initial Selection of Technologies
The EuroScan database was used to select an initial long list of new and emerging health technologies, added to the database in the previous 6 months (July to December 2007), for potential inclusion in the first issue of the newsletter. We entered (Excel spreadsheet) the following information on each of the technologies: Technology name, Company/Developer, Technology description, Patient indications, Stage of development, Technology type, Technology use, Number of patients, Cost, Existing technology, and Reason for entry on the EuroScan database.
This information constituted Part A of the spreadsheet. Each technology was considered: in the case of pharmaceuticals, already licensed or within 6 months of approval; and in the case of nonpharmaceuticals, already diffused in some EU-countries (although this information was often difficult to obtain).
The list was then edited to provide as much information as possible to the prioritization panel. The list grouped similar technologies so that a particular class of drug, type of technology, or technologies aimed at the same disease group could be compared. Particular attention was given to providing up-to-date information on the stage of development, number of patients, and cost. This resulted in a list of 104 health technologies for the pilot issue and 73 for the pilot first issue of the newsletter.
Significance Criteria and Scoring System
Using criteria developed by EuroScan we developed significance criteria to be applied to each technology in the list and a scoring system. The significance criteria were piloted and revised following feedback from the prioritization panel after the first round of selecting technologies to be included in the pilot newsletter. The significance criteria shown in Table 1 constituted headings in part B of the Excel spreadsheet. Scoring was linked with the response, giving a higher score to responses that indicated a greater impact and a zero score to responses that indicated an uncertain or low impact.
Table 1. Scoring of Potential Impact of the Technology (Part B)
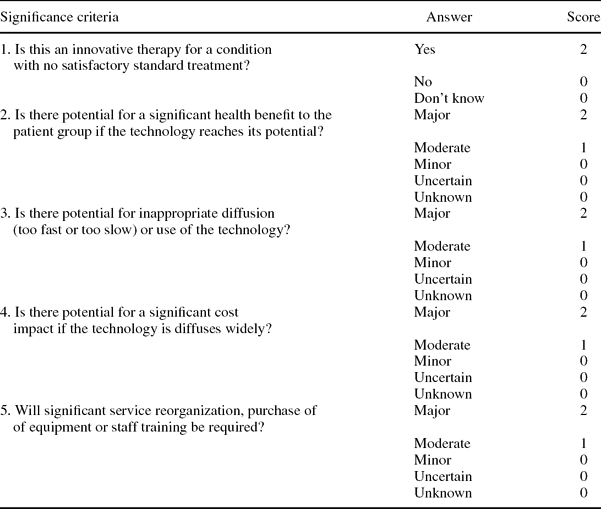
Members of the prioritization panel could also express their overall opinion of the technology—based on information in the spreadsheet and their responses regarding impact of the technology—by saying if the technology should be included and at what level, given the aims of the newsletter. Part C of the spreadsheet presents these questions, and Table 2 shows the scoring.
Table 2. Scoring on Newsletter Details (Part C)
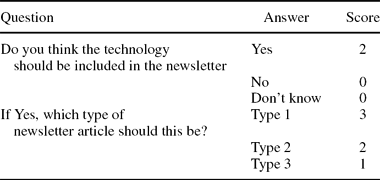
Prioritizing Technologies for Inclusion in the Newsletter
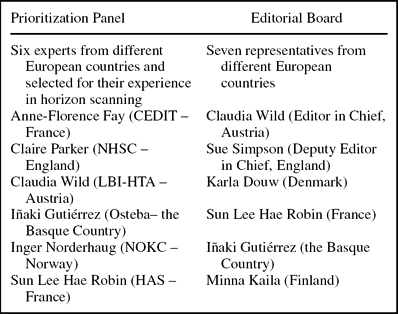
A prioritization panel comprised of EuroScan members and representatives from EUnetHTA WP7 was established (Box 2). Members of the panel were all involved in early awareness and alert activities, so they had skills in predicting the impact of a technology with limited information as provided in the spreadsheet. Panel members were sent the spreadsheet of technologies and asked to independently consider each technology against the significance criteria. They were also sent instructions for using the spreadsheet and definitions of the terms used.
Box 2. Prioritization Panel and Editorial Board
Collation of Results
Results were recorded and combined to help determine the potential impact and rank of each health technology. Scores from each panel member were added to give a possible total of ten from part B and five from part C for each technology. In part B, a score of 0 to 3 indicated a potentially low impact technology, 4 to 6 indicated a potentially important technology, and 7 to 10 indicated a potentially highly significant technology. In part C a score of: 5 indicated a technology that should be considered a Type 1 technology for the newsletter, 4 indicated a technology that should be considered a Type 2 technology for the newsletter, 3 indicated a technology that should be considered a Type 3 technology for the newsletter, and 0 indicated that the technology should not be included in the newsletter. Individual member's scores were combined for each technology and averaged. The average scores for all of the health technologies listed in the spreadsheet were reviewed together to determine which technologies should be considered for the newsletter and for what type of article. The results were sent to an editorial board (Box 2) for their views on which technologies should be included in the newsletter based on the information provided.
Production of the Newsletter
After the health technologies to be included in the newsletter had been selected and the technology types were agreed on, writing of the articles commenced. For each article, this involved referring to the original entry in the EuroScan database, searching the World Wide Web for more recent information, checking commercial databases (e.g., PharmaProjects, Adis, etc) for the latest activities on pharmaceuticals, searching bibliographic databases (e.g., MEDLINE) for recent publications, and in some cases contacting the original author of the EuroScan entry. Articles were written in English.
RESULTS
Feedback on the Newsletter
The pilot newsletter and a questionnaire were sent to EUnetHTA WP7 members with the request to distribute it to decision makers (at least three) at the national, regional, and local levels to reach a wide audience. The questionnaire was sent to twenty-three EUnetHTA Associated Partners (April 7–May 30, 2007). They were asked to forward the questionnaire to two to three decision makers in their respective countries. We asked for feedback on relevance, content, timeliness, readability, and format of the newsletter. Forty (56 percent) answered. Responses were sent by people involved in regulation, reimbursement, planning, research, and clinical practice. Most respondents (85 percent) spoke English as a second language. The majority found the newsletter relevant (75 percent), agreed the newsletter contained information on the potential effects of new technologies (75 percent), agreed the articles were sufficiently up-to-date (87.5 percent), found the text easy to understand (90 percent), and found the articles clearly structured (92.5 percent). Fewer respondents agreed that the articles focused on substantial issues (52.5 percent). Despite this positive response, several respondents wanted more information about the effectiveness, cost effectiveness, and potential impact of the technology. A substantial criticism concerned timeliness, as several technologies had already been introduced in the healthcare system because the technologies had been chosen for inclusion in the newsletter. The first issue of On the Horizon, a newsletter produced by EUnetHTA in collaboration with EuroScan and the NHSC in England, was published in 2008 and presented twelve technologies ranging from buccal insulin for diabetes to nicotine vaccines for smoking cessation (http://www.eunethta.net/Communication/Newsletter_WP7_2008).
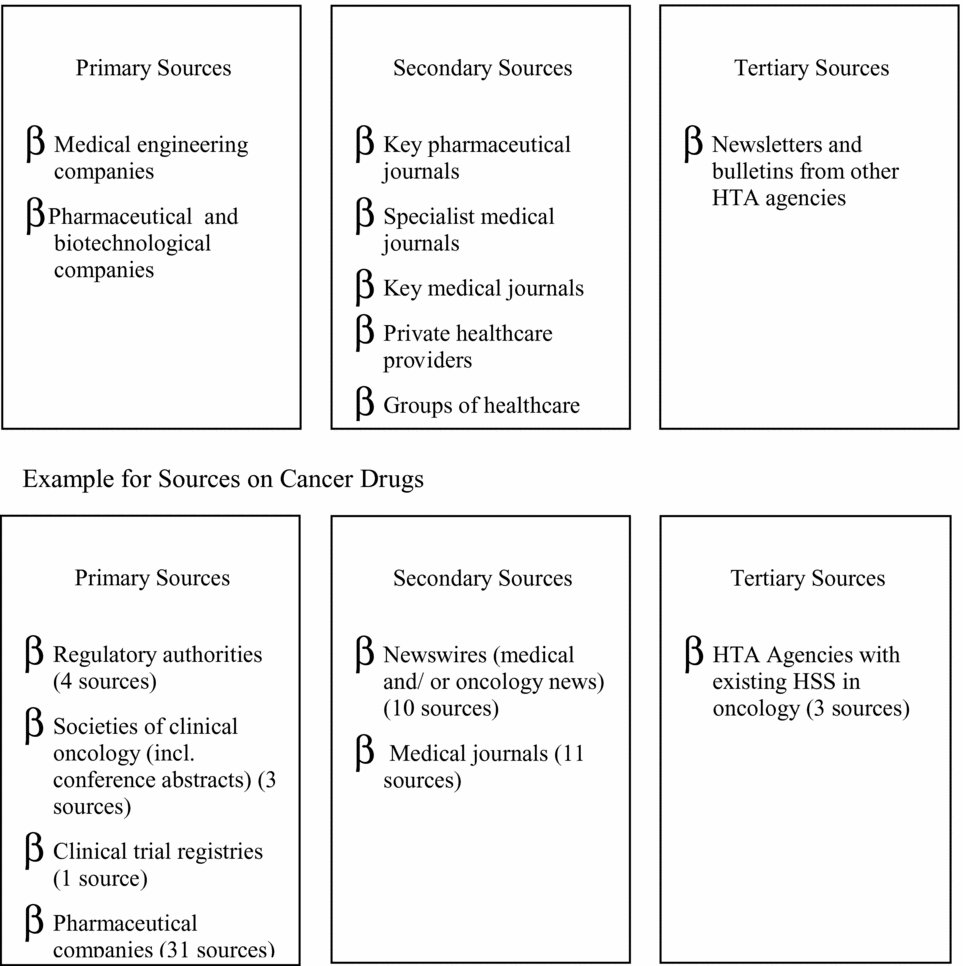
Figure 1. Potential information sources and examples of categories of sources for cancer drugs (Reference Geiger-Gritsch8; Reference Wild and Langer17).
DISCUSSION
Future Identification and Priority Setting Processes
The objective of EUnetHTA WP 7/B was to draw on the experience and know-how of EuroScan to provide a European newsletter with early alerts on emerging or new health technologies. The supposed added value to the EuroScan members’ activities in scanning, identifying, collating data, and producing early assessment papers would be the collection of information in a unique format and its wide distribution by means of the EUnetHTA Partners. Two-thirds of the then fifteen EuroScan members were involved in planning and designing the newsletter or commenting on it. Despite the seemingly facile intention, several obstacles had to be faced. In comparison with the conclusions of Douw et al. in 2006 (Reference Douw, Vondeling and Oortwijn5) on priority setting methods used in horizon scanning, it was concluded that the method for priority setting developed for the EUnetHTA newsletter is now the only formal priority setting method, or at least the only one published in this field. What this method adds, as opposed to an informal method, is that it addresses the same criteria for each potentially significant technology, it measures these criteria (i.e., major, moderate, minor impact), it scores the criteria, and it uses the final score to determine if a technology will be included in the newsletter (i.e., if it is prioritized). Hence, the criteria are applied more consistently and more transparently, which was Douw et al.'s major critique regarding the current methods of selecting technologies in horizon scanning systems. A further increase in transparency and consistency would, however, be achieved if the criteria could be validated, which this project has not yet done. Those prioritizing potentially significant new technologies appear to have differing interpretations of what constitutes a “major potential health benefit” as compared with a “moderate or minor potential health benefit”. When national prioritization exercises are undertaken, they often happen in a group setting that allows experts to have an evolving discussion in which their opinions might change toward consensus. In the further development of a European-wide prioritization process, a discussion forum might be an element to be added, but it must be balanced against the possibility of losing transparency.
An important issue for all services providing information on new and emerging health technologies, and consequently for a European newsletter, is whether the information complements useful policy advice for the EU Member States and meets the needs of the intended audience. EuroScan, EUnetHTA, and InnoHTA (another EU project 2007/08) all aimed to address uncertainty and the lack of sound information in early stages of a technology. Although each has made valuable contributions to the field of horizon scanning, the issue of trading off certainty for being early remains to be resolved in a methodologically sound way. The question is whether this needs to be done in the context of horizon scanning aimed only at providing early awareness information. What may be more important in the context of the EU-wide newsletter is whether the scope or objective of the information service corresponds with the identified technologies and those prioritized for assessment and later disseminated.
The scope of this EUnetHTA Project was to inform about “high volume, costly, and rapidly developing emerging health technologies that are at an early stage of development and which may have a significant impact on health care in the EU.” The main source of new and emerging technologies to fulfill this objective came from EuroScan member agencies by means of the EuroScan database. EuroScan's prioritization criteria were used to select the technologies to be included in the newsletter. As EuroScan members have a wide range of customers and varying coverage, there would have been some preselection/filtering, resulting in a list of selected technologies for the newsletter that would differ from a list derived through other sources. Although a possibility, it is unlikely that EuroScan would miss any major technological development that could impact on European health systems because it includes fifteen member agencies from all regions in the Western world (with diverse audiences and broadly inclusive coverage systems). However, for an EU-wide information service to respond to the needs of all EU Member States, any future project would need to investigate whether the original objective actually reflects the preferences of all EU Member States, including high, middle-, and low-income countries.
CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
The intent of EUnetHTA WP7/B was to develop an EU-wide newsletter on new and emerging health technologies. Because such a newsletter would be highly visible and have the potential to impact on agenda setting throughout Europe, considerable effort was put into developing transparent processes to select topics for the newsletter and to involve a wide range of European HTA experts in the prioritization process. However, less attention was given to the specific information needs of the intended audience. Feedback on the pilot newsletter (forty respondents from ten European countries) made it obvious that users of the newsletter lacked understanding of what kind of information is available in the early stages of a health technology's development; they wanted more information than could be provided on cost effectiveness, licensing, etc. We found that the ambitions of what can be provided and the illusion of what can be achieved by early information must be articulated explicitly and honestly. The essential discussions of “value for money,” “maximizing health gain,” or “societal value” definitely overload the idea of “alerting” about emerging technologies.
Second, the audience had very diverse interests, for example, some wanting information only on devices, others on pharmaceuticals. Third, the practicality of EU-wide involvement of experts for scoring and prioritization was a time-consuming process that is difficult to organize in the present international constellation of EAASs and hinders the production of timely information. The aim of wider dissemination of information on new and emerging technologies remains, but the methods for doing this in a way that satisfies intended audiences need further development.
Two options might be pursued to collaboratively establish an EU newsletter on new and emerging health technologies. The first would be to investigate the various interests through a consensus method involving representatives of all relevant EU Member States: An electronic information service “on-demand” might be a solution closer to the actual needs. The second would be to pursue EuroScan's earlier idea of developing a core set of early awareness information on technologies in a database (e.g., derived from EuroScan's database) to help HTA agencies in EU Member States develop early assessments fitting to their specific jurisdictions. In any case, sharing information on emerging and new health technologies remains a top priority for collaboration.
CONTACT INFORMATION
Claudia Wild, Dr. phil. (claudia.wild@hta.lbg.ac.at), Director, Ludwig Boltzmann Institute of Health Technology Assessment, Garnisongasse 7/20, 1090 Vienna, Austria
Sue Simpson, PhD (s.l.simpson.20@bham.ac.uk), Research Fellow, Unit of Public Health, Biostatistics and Epidemiology, University of Birmingham, Edgbaston, Birmingham, B15 2TT, UK
Karla Douw, PhD (kdo@cast.sdu.dk), Consultant, Centre for Applied Health Services Research and Technology Assessment, University of Southern Denmark, 9, Winsloewsvej, Odense, 5000, Denmark
Sabine Geiger-Gritsch, Dr. scient.med., MMag. pharm. (sabine.geiger-gritsch@hta.lbg.ac.at), Senior Scientist, Ludwig Boltzmann Institute of Health Technology Assessment, Garnisongasse 7/20, 1090 Vienna, Austria; Senior Scientist, Institute of Public Health, Medical Decision Making & Health Technology Assessment, University for Health Sciences, Medical Informatics and Technology, EWZ 1, 6060 Hall i.T., Austria
Stefan Mathis, Dr. med. univ., Dipl. Ing. (stefan.mathis@hta.lbg.ac.at), Senior Researcher, Ludwig Boltzmann Institute of Health Technology Assessment, Garnisongasse 7, 1090 Vienna, Austria
Thomas Langer, Dipl. Sowi (langer@azq.de), Senior Researcher, Ärztliches Zentrum für Qualität in der Medizin, Wegelystr. 3/Herbert-Lewin-Platz, Berlin, Germany, 10623









