Article contents
Zn nanodot patterning in borosilicate glasses by electron irradiation
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 May 2015
Abstract
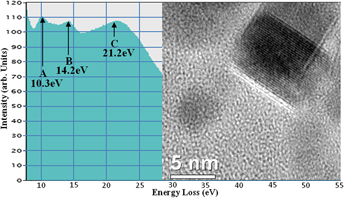
Metallic zinc nanoparticles are generated in two compositional ranges of borosilicate glasses upon 200 and 300 keV electron beam irradiation in a transmission electron microscope. Irradiation effects are studied either with a stationary electron beam as a time series or with spatially varying beams for line-scan patterning. The size of the zinc nanodots formed is inversely related to the distance from the center of the electron beam, and growth from 5 to 50 nm over time via ripening can be observed. Line-scan patterning via both thermal gun and field emission gun electron irradiation has been successfully achieved. Our findings also show the occurrence of self-organized particle ordering, such as formation of chains. Metal nanoparticles have a tendency to migrate toward the glass fragment center, unless high intensity radiation ablates the glass matrix, when Zn particles remain decorating the surface. High-resolution lattice imaging, scanning transmission electron microscopy, and electron energy loss spectroscopy are used to confirm particle identity.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2015
References
REFERENCES
- 7
- Cited by




