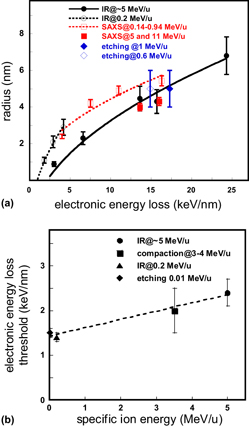
Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Zarkadoula, Eva
Toulemonde, Marcel
and
Weber, William J.
2015.
Additive effects of electronic and nuclear energy losses in irradiation-induced amorphization of zircon.
Applied Physics Letters,
Vol. 107,
Issue. 26,
Madauß, Lukas
Ochedowski, Oliver
Lebius, Henning
Ban-d’Etat, Brigitte
Naylor, Carl H
Johnson, A T Charlie
Kotakoski, Jani
and
Schleberger, Marika
2016.
Defect engineering of single- and few-layer MoS
2
by swift heavy ion irradiation
.
2D Materials,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 1,
p.
015034.
Toulemonde, M.
Assmann, W.
and
Trautmann, C.
2016.
Electronic sputtering of vitreous SiO2: Experimental and modeling results.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms,
Vol. 379,
Issue. ,
p.
2.
Radović, I Bogdanović
Buljan, M
Karlušić, M
Jerčinović, M
Dražič, G
Bernstorff, S
and
Boettger, R
2016.
Modification of semiconductor or metal nanoparticle lattices in amorphous alumina by MeV heavy ions.
New Journal of Physics,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 9,
p.
093032.
Dufour, Christian
and
Toulemonde, Marcel
2016.
Ion Beam Modification of Solids.
Vol. 61,
Issue. ,
p.
63.
Vlasukova, L.
Komarov, F.
Parkhomenko, I.
Yuvchenko, V.
Milchanin, O.
Mudryi, A.
Zyvul'ko, V.
Dauletbekova, A.
Alzhanova, A.
and
Akilbekov, A.
2017.
Photoluminescence and enhanced chemical reactivity of amorphous SiO2 films irradiated with high fluencies of 133-MeV Xe ions.
Vacuum,
Vol. 141,
Issue. ,
p.
15.
Kucheyev, S. O.
and
Shin, S. J.
2017.
Ion-beam-induced planarization, densification, and exfoliation of low-density nanoporous silica.
Applied Physics Letters,
Vol. 111,
Issue. 13,
Rivera, Antonio
Olivares, José
Prada, Alejandro
Crespillo, Miguel L.
Caturla, María J.
Bringa, Eduardo M.
Perlado, José M.
and
Peña-Rodríguez, Ovidio
2017.
Permanent modifications in silica produced by ion-induced high electronic excitation: experiments and atomistic simulations.
Scientific Reports,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 1,
Zdorovets, M V
Kadyrzhanov, D B
Kenzhina, I E
Ivanov, I A
and
Kozlovskiy, A L
2018.
Study of irradiation effect of Xe+22and Kr+14ions on structural properties of Zn nanotubes.
Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 12,
p.
125301.
Dauletbekova, A.
Kozlovskyi, A.
Akilbekov, A.
Seitbayev, A.
and
Alzhanova, A.
2018.
Synthesis of ZnO nanocrystals in a-SiO2/Si ion track templates.
Surface and Coatings Technology,
Vol. 355,
Issue. ,
p.
11.
Rath, Haripriya
Dash, B. N.
Benyagoub, A.
and
Mishra, N. C.
2018.
Sensitivity of Anatase and Rutile Phases of TiO2 to ion irradiation: Examination of the applicability of Coulomb Explosion and Thermal Spike Models.
Scientific Reports,
Vol. 8,
Issue. 1,
Yakimchuk, D. V.
Kaniukov, E. Yu.
Bundyukova, V. D.
and
Demyanov, S. E.
2018.
Plasmon-active silver nanostructures in the pores of ion-track template of SiO2 on silicon.
Doklady of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus,
Vol. 62,
Issue. 5,
p.
615.
Zdorovets, M. V.
and
Kozlovskiy, A. L.
2018.
Argon ion irradiation effect on Zn nanotubes.
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 5,
p.
3621.
Akilbekov, A
Dauletbekova, A
Baimukhanov, Z.
Kozlovskyi, A
Giniyatova, Sh
Karipbayev, Zh
Usseinov, A
and
Seitbayev, A
2018.
Structure of zinc oxide nanocrystals in track templates.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
Vol. 1115,
Issue. ,
p.
032084.
Karlušić, M.
Škrabić, M.
Majer, M.
Buljan, M.
Skuratov, V.A.
Jung, H.K.
O. Gamulin
and
Jakšić, M.
2019.
Infrared spectroscopy of ion tracks in amorphous SiO2 and comparison to gamma irradiation induced changes.
Journal of Nuclear Materials,
Vol. 514,
Issue. ,
p.
74.
Dauletbekova, Alma
Vlasukova, Liudmila
Baimukhanov, Zein
Akilbekov, Abdirash
Kozlovskyi, Artem
Giniyatova, Sholpan
Seitbayev, Aibek
Usseinov, Abai
and
Akylbekova, Aiman
2019.
Synthesis of ZnO Nanocrystals in SiO2/Si Track Template: Effect of Electrodeposition Parameters on Structure.
physica status solidi (b),
Vol. 256,
Issue. 5,
Barannik, E.
Bainaiev, O.
Zhurenko, V.
Kononenko, S.
and
Kalantaryan, O.
2020.
Time dependence of silica optical properties during the implantation of fast hydrogen ions: Computer modeling.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms,
Vol. 471,
Issue. ,
p.
105.
Lang, Maik
Djurabekova, Flyura
Medvedev, Nikita
Toulemonde, Marcel
and
Trautmann, Christina
2020.
Comprehensive Nuclear Materials.
p.
485.
Matsunami, Noriaki
Sataka, Masao
Okayasu, Satoru
and
Tsuchiya, Bun
2021.
Modification of SiO2, ZnO, Fe2O3 and TiN Films by Electronic Excitation under High Energy Ion Impact.
Quantum Beam Science,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 4,
p.
30.
Garcia Toro, Maria C.
Crespillo, Miguel L.
Olivares, Jose
and
Graham, Joseph T.
2021.
Anisotropic nanostructure formation by vapor etching of ion tracks in α-quartz.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms,
Vol. 498,
Issue. ,
p.
52.