No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
CONDITIONS FOR A SCHUNCK CLASS TO BE A FORMATION
Part of:
General nonassociative rings
Representation theory of groups
Lie algebras and Lie superalgebras
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 September 2014
Abstract
Core share and HTML view are not available for this content. However, as you have access to this content, a full PDF is available via the ‘Save PDF’ action button.
A Schunck class 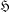 $\mathfrak{H}$ is determined by the class
$\mathfrak{H}$ is determined by the class 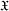 $\mathfrak{X}$ of primitives contained in
$\mathfrak{X}$ of primitives contained in 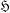 $\mathfrak{H}$. We give necessary and sufficient conditions on
$\mathfrak{H}$. We give necessary and sufficient conditions on 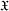 $\mathfrak{X}$ for
$\mathfrak{X}$ for 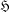 $\mathfrak{H}$ to be a saturated formation.
$\mathfrak{H}$ to be a saturated formation.
Keywords
MSC classification
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © 2014 Australian Mathematical Publishing Association Inc.
References
Barnes, D. W., ‘First cohomology groups of p-soluble groups’, J. Algebra 46 (1977), 298–302.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Barnes, D. W., Schunck classes of restricted Lie algebras, arXiv:mathRA/0610609 (2006).Google Scholar
Barnes, D. W., ‘On locally defined formations of soluble Lie and Leibniz algebras’, Bull. Aust. Math. Soc. 86 (2012), 322–326.Google Scholar
Barnes, D. W., ‘Schunck classes of soluble Leibniz algebras’, Comm. Algebra 41 (2013), 4046–4065.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Barnes, D. W. and Gastineau-Hills, H. M., ‘On the theory of soluble Lie algebras’, Math. Z. 106 (1968), 343–354.Google Scholar
Gaschütz, W., ‘Zur Theorie der endlichen auflösbaren Gruppen’, Math. Z. 80 (1963), 300–305.CrossRefGoogle Scholar




