A number of studies suggest that mortality in patients admitted to hospitals during the weekend is higher than in those admitted on a weekday [Reference Bell and Redelmeier1–Reference Mohammed3]. Differences in severity of illness, staffing and elective admissions have been hypothesized as determinants of this association. This ‘weekend phenomenon’ has been studied in medical and surgical patients and seems to affect timing of procedures, length of stay and rates of re-admission [Reference Gallerani4, Reference de Groot5]. However, results vary depending on the disease or population studied. In the case of infections, it is possible that the ‘weekend phenomenon’ results in delays of diagnosis, initiation of appropriate antibiotic therapy or, in the case of sepsis, initiation of early goal-directed therapy. In a large retrospective single-centre cohort, no mortality differences were observed for septicemia and pneumonia between weekend and weekday admissions [Reference Bell and Redelmeier1]. Other infectious diseases such as pneumonia and meningitis have exhibited less favourable outcomes in patients admitted on weekends [Reference Goldacre6, Reference Chang and Tung7]. Although urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in both outpatient and inpatient settings, the effect of weekend diagnosis on its outcome has not been studied to date. Our goal was to compare outcomes between patients diagnosed during the weekend vs. those diagnosed on a weekday.
We performed a post-hoc analysis using data from a prospective cohort study of hospitalized patients with E. coli bacteriuria [Reference Marschall8]. A subgroup of patients with symptomatic E. coli UTI (cystitis and pyelonephritis) was identified in order to evaluate differences in length of stay, intensive care unit (ICU) transfer within 3 days of diagnosis, development of bacteraemia within 1 day of diagnosis, development of sepsis and sepsis-induced hypotension, choices of antibiotic therapy, and in-hospital mortality between those diagnosed during the weekend and those diagnosed on a weekday. Cystitis was defined as presence of dysuria, frequency, or urinary retention/hesitancy (without signs of pyelonephritis) and pyelonephritis was defined as presence of flank pain or tenderness and/or fever [Reference Marschall8, Reference Warren9]. Patients were enrolled between 1 August 2009 and 31 July 2010, at a 1250-bed teaching hospital in St Louis, Missouri. ‘Weekend’ was defined as the period from 00:00 hours Saturday to 23:59 hours Sunday [Reference Laupland10]. Adequacy of antibiotic therapy was defined as pathogen-directed treatment with matching antibiotic susceptibilities. Data analysis was performed using SPSS v. 18 (SPSS Inc., USA). We performed univariate comparisons in categorical variables using the χ 2 test or Fisher's exact test as appropriate. Comparisons between continuous independent variables were performed using Student's t test or Mann–Whitney U test as appropriate. A two-sided P value of <0·05 was considered significant. Variables with a P < 0·05 on univariate testing were entered into a multivariate logistic regression model in one step. The study was approved by the Washington University Human Research Protection Office.
During the 12-month study period, 400 patients with symptomatic E. coli UTI (cystitis and/or pyelonephritis) were identified. Of these, 313 (78·3%) were women and 223 (55·8%) were white. The mean age at diagnosis was 60 years (range 18–102 years). Community-acquired UTI was encountered in 271 (67·8%) of these patients. In total, 109 patients (27·3%) were diagnosed during the weekend. The median admission Charlson comorbidity score at admission was 2 (range 0–13). There was no statistically significant difference in development of sepsis (65·1% vs. 56·7%, P = 0·1), sepsis-induced hypotension (22% vs. 18·9%, P = 0·4) and multi-organ dysfunction (0·3% vs. 0%, P = 0·1) between those diagnosed during the weekend and those diagnosed on a weekday. For those who had blood cultures performed, there was no difference in the rates of bacteraemia (24% vs. 15%, P = 0·1). Appropriateness of initial antibiotic therapy was higher in the weekend group (92% vs. 81%, P = 0·01) while timing of antibiotic therapy and transfer to ICU were not different between the two groups (data not shown). Median length of hospitalization was 6·6 days for those diagnosed during the weekend vs. 6·7 days for weekdays (P = 0·9). Overall mortality rate was 3·8% (n = 15) and crude in-hospital mortality was not different between weekend and weekday groups (5·5% vs. 3·1%, respectively, P = 0·4). Development of sepsis (87% vs. 58%, P = 0·02), sepsis-induced hypotension (73% vs. 18%, P < 0·01), ICU stay (67% vs. 10%, P < 0·01) and multi-organ dysfunction (7% vs. 0%, P = 0·03) were associated with mortality. In multivariate analysis, independent predictors of mortality were sepsis-induced hypotension and ICU admission (Table 1). Additionally, a separate multivariate analysis where weekend diagnosis was based on the date and time culture results were reported (rather than the collection date) generated similar results.
Table 1. Multivariate analysis of factors associated with in-hospital mortality in 400 patients with E. coli urinary tract infection
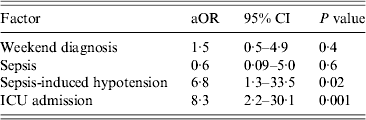
aOR, Adjusted odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; ICU, intensive care unit.
All variables indicated above were included in a binary logistic regression model. The variance inflation factor values for the variables did not suggest multicollinearity. The Hosmer–Lemeshow test for goodness-of-fit was non-significant (P = 0·9).
In this study, ICU admission and sepsis-induced hypotension were independent predictors of mortality. However, weekend diagnosis was not associated with increased mortality. A series of studies with large numbers of patients have demonstrated an increased mortality associated with weekend hospitalization [Reference Bell and Redelmeier1, Reference Barba2]. Limitations of those studies include selection bias, unmeasured confounding factors (severity of illness, differences in and appropriateness of management) and inclusion of multiple conditions. Our study is the first to focus exclusively on a common infectious disease for which management guidelines are readily available to healthcare providers. We found that, in our cohort, markers of severity of illness (i.e. hypotension and ICU admission) were most predictive of mortality. This confirms findings in earlier studies [Reference Chang and Tung7, Reference Ginde, Rhee and Katz11]. Despite having better rates of appropriate antibiotic therapy, patients diagnosed during the weekend had somewhat higher rates of bacteraemia, ICU admission, sepsis and sepsis-induced hypotension. However, these differences were not statistically significant. Further, compared to their counterparts, patients with hospital-acquired UTI and catheter-associated UTI had significantly higher rates of ICU admission but no statistically significant differences in rates of sepsis or sepsis-induced hypotension (data not shown). Whether catheter-associated UTIs are associated with increased morbidity and mortality in critically ill patients remains unclear [Reference Chant12]. Our regression model might be limited by the small number of patient deaths, as it has been suggested that at least 10 events per independent variable should be included in the model [Reference Peduzzi13]. However, a rigorous study examining this particular matter concluded that in many applications the ‘rule of 10’ may be too conservative and showed that 5–9 endpoint events per parameter are, in general, acceptable [Reference Vittinghoff and McCulloch14]. Moreover, the results of the goodness-of-fit test we employed (Hosmer–Lemeshow) suggest that the model is a satisfactory fit to the data. This is, to our knowledge, the first study of a single medical condition to address multiple potential, modifiable and non-modifiable determinants of outcome in relationship to the ‘weekend phenomenon’. Our findings suggest that patient-specific factors such as severity of illness determine outcomes in E. coli UTIs rather than the time of diagnosis.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
J.M. was supported by the NIH CTSA (UL1RR024992) and was the recipient of a KL2 Career Development Grant (KL2RR024994); he is currently supported by a BIRCWH KL2 career development award (5K12HD001459-13). He is also the section leader for a subproject of the CDC Prevention Epicenters Program Grant CU54 CK 000162; PI: Fraser). In addition, J.M. is funded by the Barnes-Jewish Hospital Patient Safety and Quality Fellowship Program and a research grant from the Barnes-Jewish Hospital Foundation and Washington University's Institute of Clinical and Translational Sciences (ICTS). J.P.H. was supported by a Burroughs-Wellcome Career Award for Medical Scientists.
We thank Marilyn Piccirillo, Claire Tourjee and Kyle Ota who assisted with the collection of patient data.
DECLARATION OF INTEREST
None.





