Article contents
The mean electromotive force generated by elliptic instability
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 July 2012
Abstract
The mean electromotive force (EMF) associated with exponentially growing perturbations of an Euler flow with elliptic streamlines in a rotating frame of reference is studied. We are motivated by the possibility of dynamo action triggered by tidal deformation of astrophysical objects such as accretion discs, stars or planets. Ellipticity of the flow models such tidal deformations in the simplest way. Using analytical techniques developed by Lebovitz & Zweibel (Astrophys. J., vol. 609, 2004, pp. 301–312) in the limit of small elliptic (tidal) deformations, we find the EMF associated with each resonant instability described by Mizerski & Bajer (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 632, 2009, pp. 401–430), and for arbitrary ellipticity the EMF associated with unstable horizontal modes. Mixed resonance between unstable hydrodynamic and magnetic modes and resonance between unstable and oscillatory horizontal modes both lead to a non-vanishing mean EMF which grows exponentially in time. The essential conclusion is that interactions between unstable eigenmodes with the same wave-vector 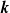 can lead to a non-vanishing mean EMF, without any need for viscous or magnetic dissipation. This applies generally (and not only to the elliptic instabilities considered here).
can lead to a non-vanishing mean EMF, without any need for viscous or magnetic dissipation. This applies generally (and not only to the elliptic instabilities considered here).
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2012
References
- 9
- Cited by




