Article contents
Improved structural and electrical properties of thin ZnO:Al films by dc filtered cathodic arc deposition
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 November 2011
Abstract
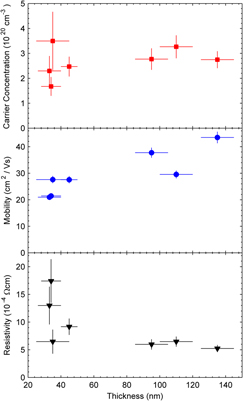
Transparent conducting oxide films are usually several 100-nm thick to achieve the required low sheet resistance. In this study, we show that the filtered cathodic arc technique produces high-quality low-cost ZnO:Al material for comparably smaller thicknesses than achieved by magnetron sputtering, making arc deposition a promising choice for applications requiring films less than 100-nm thick. A mean surface roughness less than 1 nm is observed for ZnO:Al films less than 100-nm thick, and 35-nm-thick ZnO:Al films exhibit Hall mobility of 28 cm2/Vs and a low resistivity of 6.5 × 10−4 Ωcm. Resistivity as low as 5.2 × 10−4 Ωcm and mobility as high as 43.5 cm2/Vs are obtained for 135-nm films.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 27 , Issue 5: Focus Issue: Plasma and Ion-Beam Assisted Materials Processing , 14 March 2012 , pp. 857 - 862
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2011
References
REFERENCES
- 3
- Cited by




