Article contents
Lagrangian acceleration measurements in convective thermal turbulence
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 06 January 2012
Abstract
We report the first experimental study of Lagrangian acceleration in turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection, using particle tracking velocimetry. A method has been developed to quantitatively evaluate and eliminate the uncertainties induced by temperature and refraction index fluctuations caused by the thermal plumes. It is found that the acceleration p.d.f. exhibits a stretched exponential form and that the probability for large magnitude of acceleration in the lateral direction is higher than those in the vertical directions, which can be attributed to the vortical motion of the thermal plumes. The local acceleration variance 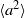 was obtained for various values of the three control parameters: the Rayleigh number
was obtained for various values of the three control parameters: the Rayleigh number 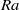 (
(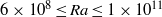 ), the Prandtl number
), the Prandtl number 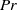 (
(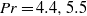 and 6.1) and the system size
and 6.1) and the system size 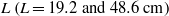 . These were then compared with the theoretically predicted dependence on these parameters for buoyancy-dominated turbulent flows and for homogeneous and isotropic turbulence, respectively. It is found that
. These were then compared with the theoretically predicted dependence on these parameters for buoyancy-dominated turbulent flows and for homogeneous and isotropic turbulence, respectively. It is found that 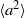 in the central region is dominated by contributions from the turbulent background rather than from the buoyancy force, and the Heisenberg–Yaglom relation holds in this region. From this, we obtain the first experimental results of the constant
in the central region is dominated by contributions from the turbulent background rather than from the buoyancy force, and the Heisenberg–Yaglom relation holds in this region. From this, we obtain the first experimental results of the constant 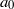 of the acceleration variance in the micro-scale Reynolds number range
of the acceleration variance in the micro-scale Reynolds number range 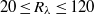 , which fills a gap in this constant in the lower
, which fills a gap in this constant in the lower 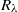 end from the experimental side, and provides possible constraints for its high
end from the experimental side, and provides possible constraints for its high 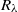 behaviour if a certain fitting function is attempted. In addition, acceleration correlation functions were obtained for different
behaviour if a certain fitting function is attempted. In addition, acceleration correlation functions were obtained for different 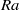 . It is found that the zero crossing time of acceleration correlation functions is at
. It is found that the zero crossing time of acceleration correlation functions is at 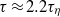 (
(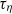 is the Kolmogorov time scale) over the range of
is the Kolmogorov time scale) over the range of 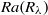 spanned in our experiments, which is the same as the simulation results in isotropic turbulence, and the exponential decay time
spanned in our experiments, which is the same as the simulation results in isotropic turbulence, and the exponential decay time 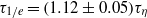 , which is larger than
, which is larger than 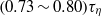 found experimentally for other types of turbulent flows with larger
found experimentally for other types of turbulent flows with larger 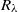 .
.
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2012
References
- 46
- Cited by




