Article contents
Emission and absorption cross section spectra of Er3+ in LiNbO3 crystals codoped with indium
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 April 2011
Abstract
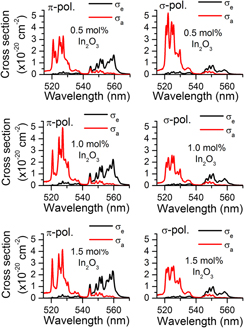
We have measured at room temperature polarized visible and near-infrared and unpolarized mid-infrared (2.7 μm) emission spectra of Er3+ in LiNbO3 (LN) crystals grown from congruent melts doped with 0.0/0.5, 0.5/0.5, and 1.0/0.5 mol%/mol% In2O3/Er2O3. From the measured emission spectra, the emission and absorption cross section spectral distributions were analyzed based on McCumber theory and discussed in comparison with those spectra of only Er-doped LN bulk material and/or Ti: Er: LN waveguide structure and with the results from the unpolarized absorption measurements. For the 530 and 1530 nm transitions, the cross section value, polarization dependence, and spectral shape all change from the only Er-doped material to the In–Er-codoped crystal and show definite In2O3 doping level effect. The 559, 673, 996, and 1530 nm emission lifetimes were also measured and used to evaluate nonradiative multiphonon relaxation rate. The calculated radiative, measured lifetimes, and multiphonon relaxation rate also show In-codoping effects.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2011
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by




