Article contents
Parabolic induction and restriction via 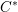 $C^{\ast }$-algebras and Hilbert
$C^{\ast }$-algebras and Hilbert 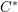 $C^{\ast }$-modules
$C^{\ast }$-modules
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 February 2016
Abstract
This paper is about the reduced group 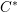 $C^{\ast }$-algebras of real reductive groups, and about Hilbert
$C^{\ast }$-algebras of real reductive groups, and about Hilbert 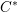 $C^{\ast }$-modules over these
$C^{\ast }$-modules over these 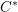 $C^{\ast }$-algebras. We shall do three things. First, we shall apply theorems from the tempered representation theory of reductive groups to determine the structure of the reduced
$C^{\ast }$-algebras. We shall do three things. First, we shall apply theorems from the tempered representation theory of reductive groups to determine the structure of the reduced 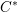 $C^{\ast }$-algebra (the result has been known for some time, but it is difficult to assemble a full treatment from the existing literature). Second, we shall use the structure of the reduced
$C^{\ast }$-algebra (the result has been known for some time, but it is difficult to assemble a full treatment from the existing literature). Second, we shall use the structure of the reduced 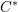 $C^{\ast }$-algebra to determine the structure of the Hilbert
$C^{\ast }$-algebra to determine the structure of the Hilbert 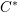 $C^{\ast }$-bimodule that represents the functor of parabolic induction. Third, we shall prove that the parabolic induction bimodule admits a secondary inner product, using which we can define a functor of parabolic restriction in tempered representation theory. We shall prove in a sequel to this paper that parabolic restriction is adjoint, on both the left and the right, to parabolic induction in the context of tempered unitary Hilbert space representations.
$C^{\ast }$-bimodule that represents the functor of parabolic induction. Third, we shall prove that the parabolic induction bimodule admits a secondary inner product, using which we can define a functor of parabolic restriction in tempered representation theory. We shall prove in a sequel to this paper that parabolic restriction is adjoint, on both the left and the right, to parabolic induction in the context of tempered unitary Hilbert space representations.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Authors 2016
References
- 15
- Cited by




