Article contents
Structure of transition classes for factor codes on shifts of finite type
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 August 2014
Abstract
Given a factor code  ${\it\pi}$ from a shift of finite type
${\it\pi}$ from a shift of finite type 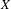 $X$ onto a sofic shift
$X$ onto a sofic shift  $Y$, the class degree of
$Y$, the class degree of  ${\it\pi}$ is defined to be the minimal number of transition classes over the points of
${\it\pi}$ is defined to be the minimal number of transition classes over the points of  $Y$. In this paper, we investigate the structure of transition classes and present several dynamical properties analogous to the properties of fibers of finite-to-one factor codes. As a corollary, we show that for an irreducible factor triple, there cannot be a transition between two distinct transition classes over a right transitive point, answering a question raised by Quas.
$Y$. In this paper, we investigate the structure of transition classes and present several dynamical properties analogous to the properties of fibers of finite-to-one factor codes. As a corollary, we show that for an irreducible factor triple, there cannot be a transition between two distinct transition classes over a right transitive point, answering a question raised by Quas.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press, 2014
References
- 6
- Cited by




