Article contents
Drag force on a liquid domain moving inside a membrane sheet surrounded by aqueous medium
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 August 2015
Abstract
We compute the drag on a circular and liquid microdomain diffusing in a two-dimensional fluid lipid bilayer membrane surrounded by a fluid above and below. Under the assumptions that the liquids are incompressible and the flow is of low Reynolds number, Stokes’ equations describe the flow in the two-dimensional membrane as well as in the surrounding three-dimensional fluid. The expression for the drag force on the liquid domain involves Fredholm integral equations of the second kind, which we numerically solve using discrete collocation method based on Chebyshev polynomials. We observe that when the domain is more viscous than the surrounding membrane (including the rigid domain case), the drag force is almost independent of the viscosity contrast between the domain and the surrounding membrane, as also observed earlier in experiments by other researchers. The mobility also varies logarithmically with Boussinesq number 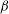 ${\it\beta}$ for large
${\it\beta}$ for large 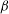 ${\it\beta}$. On the other hand, for a less viscous domain the dimensionless drag force reduces with increasing viscosity contrast, and a significant change in the drag force, from that when there is no viscosity contrast or when the domain is rigid, has been observed. Further, the logarithmic behaviour of the mobility no longer holds for less viscous domains. Our method of computing the drag force and diffusion coefficient is valid for arbitrary viscosity contrast between the domain and membrane and any domain size (subject to
${\it\beta}$. On the other hand, for a less viscous domain the dimensionless drag force reduces with increasing viscosity contrast, and a significant change in the drag force, from that when there is no viscosity contrast or when the domain is rigid, has been observed. Further, the logarithmic behaviour of the mobility no longer holds for less viscous domains. Our method of computing the drag force and diffusion coefficient is valid for arbitrary viscosity contrast between the domain and membrane and any domain size (subject to 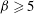 ${\it\beta}\geqslant 5$).
${\it\beta}\geqslant 5$).
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2015 Cambridge University Press
References
- 6
- Cited by





