Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Chung, D.
Marusic, I.
Monty, J. P.
Vallikivi, M.
and
Smits, A. J.
2015.
On the universality of inertial energy in the log layer of turbulent boundary layer and pipe flows .
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 7,
Hohman, T.C.
Buren, T. Van
Martinelli, L.
and
Smits, A.J.
2015.
Generating an artificially thickened boundary layer to simulate the neutral atmospheric boundary layer.
Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,
Vol. 145,
Issue. ,
p.
1.
Mouri, Hideaki
2015.
Mathematical model for logarithmic scaling of velocity fluctuations in wall turbulence.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 92,
Issue. 6,
Falkovich, Gregory
2016.
Interaction between mean flow and turbulence in two dimensions.
Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 472,
Issue. 2191,
p.
20160287.
Bobke, Alexandra
Vinuesa, Ricardo
Örlü, Ramis
and
Schlatter, Philipp
2016.
Large-eddy simulations of adverse pressure gradient turbulent boundary layers.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
Vol. 708,
Issue. ,
p.
012012.
Wang, Guohua
and
Zheng, Xiaojing
2016.
Very large scale motions in the atmospheric surface layer: a field investigation.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 802,
Issue. ,
p.
464.
Miller, M.A.
Kiefer, J.
Westergaard, C.
and
Hultmark, M.
2016.
Model Wind Turbines Tested at Full-Scale Similarity.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
Vol. 753,
Issue. ,
p.
032018.
Olsen, Michael E.
2016.
Reynolds-stress and triple-product models applied to flows with rotation and curvature.
Örlü, Ramis
Segalini, Antonio
Klewicki, Joseph
and
Alfredsson, P. Henrik
2016.
High-order generalisation of the diagnostic scaling for turbulent boundary layers.
Journal of Turbulence,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 7,
p.
664.
Laval, J.-P.
Vassilicos, J. C.
Foucaut, J.-M.
and
Stanislas, M.
2017.
Comparison of turbulence profiles in high-Reynolds-number turbulent boundary layers and validation of a predictive model.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 814,
Issue. ,
Marusic, Ivan
Baars, Woutijn J.
and
Hutchins, Nicholas
2017.
Scaling of the streamwise turbulence intensity in the context of inner-outer interactions in wall turbulence.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 10,
Cuvier, C.
Srinath, S.
Stanislas, M.
Foucaut, J. M.
Laval, J. P.
Kähler, C. J.
Hain, R.
Scharnowski, S.
Schröder, A.
Geisler, R.
Agocs, J.
Röse, A.
Willert, C.
Klinner, J.
Amili, O.
Atkinson, C.
and
Soria, J.
2017.
Extensive characterisation of a high Reynolds number decelerating boundary layer using advanced optical metrology.
Journal of Turbulence,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 10,
p.
929.
Olsen, Michael E.
and
Lillard, Randolph P.
2017.
Revised Reynolds-Stress and Triple Product Models.
Vinuesa, Ricardo
Hosseini, Seyed M.
Hanifi, Ardeshir
Henningson, Dan S.
and
Schlatter, Philipp
2017.
Pressure-Gradient Turbulent Boundary Layers Developing Around a Wing Section.
Flow, Turbulence and Combustion,
Vol. 99,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
613.
Chen, Xi
Hussain, Fazle
and
She, Zhen-Su
2017.
Predictions of canonical wall-bounded turbulent flows via a modified k–ω equation.
Journal of Turbulence,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 1,
p.
1.
Örlü, R.
Fiorini, T.
Segalini, A.
Bellani, G.
Talamelli, A.
and
Alfredsson, P. H.
2017.
Reynolds stress scaling in pipe flow turbulence—first results from CICLoPE.
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 375,
Issue. 2089,
p.
20160187.
Stanislas, Michel
2017.
Near wall turbulence: An experimental view.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 10,
Wu, Bin
Bi, Weitao
Hussain, Fazle
and
She, Zhen-Su
2017.
On the invariant mean velocity profile for compressible turbulent boundary layers.
Journal of Turbulence,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 2,
p.
186.
Diwan, Sourabh S.
and
Morrison, Jonathan F.
2017.
Spectral structure and linear mechanisms in a rapidly distorted boundary layer.
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow,
Vol. 67,
Issue. ,
p.
63.
Wang, Wenkang
Pan, Chong
and
Wang, Jinjun
2018.
Quasi-bivariate variational mode decomposition as a tool of scale analysis in wall-bounded turbulence.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 59,
Issue. 1,
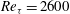 $\mathit{Re}_{{\it\tau}}=2600$ to
$\mathit{Re}_{{\it\tau}}=2600$ to 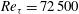 $\mathit{Re}_{{\it\tau}}=72\,500$ (
$\mathit{Re}_{{\it\tau}}=72\,500$ (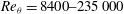 $\mathit{Re}_{{\it\theta}}=8400{-}235\,000$). The wind tunnel facility uses pressurized air as the working fluid, and in combination with MEMS-based sensors to resolve the small scales of motion allows for a unique investigation of boundary layer flow at very high Reynolds numbers. The data include mean velocities, streamwise turbulence variances, and moments up to 10th order. The results are compared to previously reported high Reynolds number pipe flow data. For
$\mathit{Re}_{{\it\theta}}=8400{-}235\,000$). The wind tunnel facility uses pressurized air as the working fluid, and in combination with MEMS-based sensors to resolve the small scales of motion allows for a unique investigation of boundary layer flow at very high Reynolds numbers. The data include mean velocities, streamwise turbulence variances, and moments up to 10th order. The results are compared to previously reported high Reynolds number pipe flow data. For 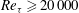 $\mathit{Re}_{{\it\tau}}\geqslant 20\,000$, both flows display a logarithmic region in the profiles of the mean velocity and all even moments, suggesting the emergence of a universal behaviour in the statistics at these high Reynolds numbers.
$\mathit{Re}_{{\it\tau}}\geqslant 20\,000$, both flows display a logarithmic region in the profiles of the mean velocity and all even moments, suggesting the emergence of a universal behaviour in the statistics at these high Reynolds numbers.




