Article contents
CONSISTENCY AND ASYMPTOTIC NORMALITY OF SIEVE ML ESTIMATORS UNDER LOW-LEVEL CONDITIONS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 April 2014
Abstract
This paper considers sieve maximum likelihood estimation of seminonparametric (SNP) models with an unknown density function as non-Euclidean parameter, next to a finite-dimensional parameter vector. The density function involved is modeled via an infinite series expansion, so that the actual parameter space is infinite-dimensional. It will be shown that under low-level conditions the sieve estimators of these parameters are consistent, and the estimators of the Euclidean parameters are 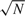 $\sqrt N$ asymptotically normal, given a random sample of size N. The latter result is derived in a different way than in the sieve estimation literature. It appears that this asymptotic normality result is in essence the same as for the finite dimensional case. This approach is motivated and illustrated by an SNP discrete choice model.
$\sqrt N$ asymptotically normal, given a random sample of size N. The latter result is derived in a different way than in the sieve estimation literature. It appears that this asymptotic normality result is in essence the same as for the finite dimensional case. This approach is motivated and illustrated by an SNP discrete choice model.
- Type
- ARTICLES
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2014
References
REFERENCES
- 9
- Cited by




