Article contents
Particle-laden flow down a slope in uniform stratification
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 August 2014
Abstract
Lock–release laboratory experiments are performed to examine saline and particle-laden flows down a slope into both constant-density and linearly stratified ambients. Both hypopycnal (surface-propagating) currents and hyperpycnal (turbidity) currents are examined, with the focus being upon the influence of ambient stratification on turbidity currents. Measurements are made of the along-slope front speed and the depth at which the turbidity current separates from the slope and intrudes into the ambient. These results are compared to the predictions of a theory that characterizes the flow evolution and separation depth in terms of the slope  $\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}s$, the entrainment parameter
$\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}s$, the entrainment parameter 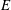 $E$ (the ratio of entrainment to flow speed), the relative stratification parameter
$E$ (the ratio of entrainment to flow speed), the relative stratification parameter 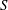 $S$ (the ratio of the ambient density difference to the relative current density) and a new parameter
$S$ (the ratio of the ambient density difference to the relative current density) and a new parameter 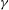 $\gamma $ defined to be the ratio of the particle settling to entrainment speed. The implicit prediction for the separation depth,
$\gamma $ defined to be the ratio of the particle settling to entrainment speed. The implicit prediction for the separation depth, 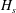 $H_s$, is made explicit by considering limits of small and large separation depth. In the former case of a ‘weak’ turbidity current, entrainment and particle settling are unimportant and separation occurs where the density of the ambient fluid equals the density of the fluid in the lock. In the latter case of a ‘strong’ turbidity current, entrainment and particle settling crucially affect the separation depth. Consistent with theory, we find that the separation depth indeed depends on
$H_s$, is made explicit by considering limits of small and large separation depth. In the former case of a ‘weak’ turbidity current, entrainment and particle settling are unimportant and separation occurs where the density of the ambient fluid equals the density of the fluid in the lock. In the latter case of a ‘strong’ turbidity current, entrainment and particle settling crucially affect the separation depth. Consistent with theory, we find that the separation depth indeed depends on 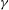 $\gamma $ if the particle size (and hence settling rate) is sufficiently large and if the current propagates many lock lengths before separating from the slope. A composite prediction that combines the explicit formulae for the separation depth for weak and strong turbidity currents agrees well with experimental measurements over a wide parameter range.
$\gamma $ if the particle size (and hence settling rate) is sufficiently large and if the current propagates many lock lengths before separating from the slope. A composite prediction that combines the explicit formulae for the separation depth for weak and strong turbidity currents agrees well with experimental measurements over a wide parameter range.
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2014 Cambridge University Press
References
Snow and Sutherland supplementary movie
Movie corresponding to experiment shown in Figures 3, 4c and 5 of a turbidity current in a stratified ambient
Snow and Sutherland supplementary movie
Movie corresponding to experiment shown in Figure 4a of a saline gravity current in a uniform density ambient
Snow and Sutherland supplementary movie
Movie corresponding to experiment shown in Figure 4b of a turbidity current in a uniform density ambient
- 26
- Cited by




